Fig. 1.
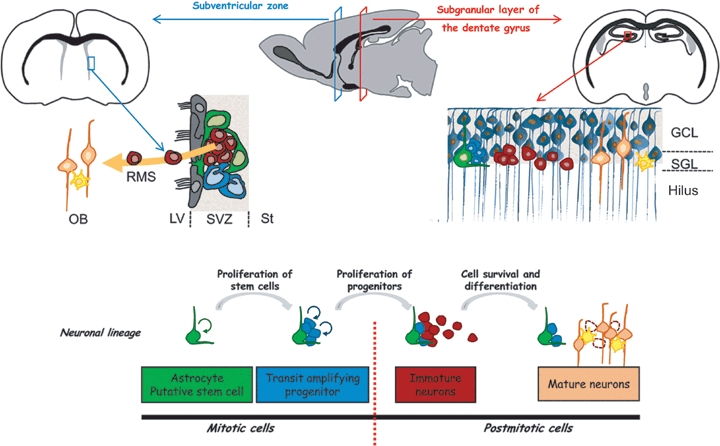
The main neurogenic areas of the adult brain. Adult neurogenesis has been described in the subventricular (SVZ)/olfactory bulb (OB) and in the hippocampal system. Representations of the different stages of adult neurogenesis that may be affected by aging; glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive astrocytes (green) have been identified as in vivo stem cells in the SVZ and stem-like cells in the dentate gyrus (DG). They divide slowly to give rise to transit amplifying progenitors (blue), which in turn generate immature cells (red) able to differentiate either into neurons (orange) or glial cells (yellow). A significant fraction of the newborn cells die during the maturation process (dotted cells). RMS, rostral migratory stream; LV, lateral ventricle; St, striatum; GCL, granule cell layer; SGL, subgranular layer.
