Fig. 3.
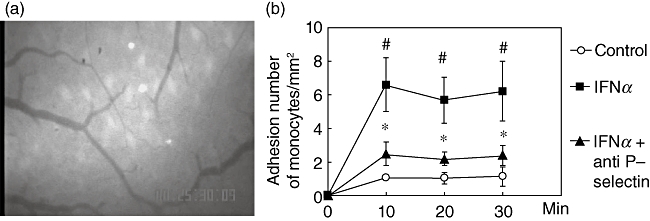
Effect of the anti-P-selectin antibody treatment on enhanced monocyte migration which was induced by interferon (IFN)-α treatment. Representative photographs of in vivo observation of monocyte migration in intestinal microvessels. The anti-P-selectin antibody treatment to IFN-α-treated animals blocked monocyte migration behaviour (a). Time–course of monocyte adhesion in the submucosal venules of small intestine. IFN-α increased monocyte adhesion significantly. Anti P-selectin antibody attenuated the increase of migration of monocytes induced by IFN-α. (b). ○: Control;  : IFN-α treated group; ▴: IFN-α+ anti P-selectin antibody-treated group; #P < 0·05 versus control; *P < 0·05 versus IFN-α-treated group.
: IFN-α treated group; ▴: IFN-α+ anti P-selectin antibody-treated group; #P < 0·05 versus control; *P < 0·05 versus IFN-α-treated group.
