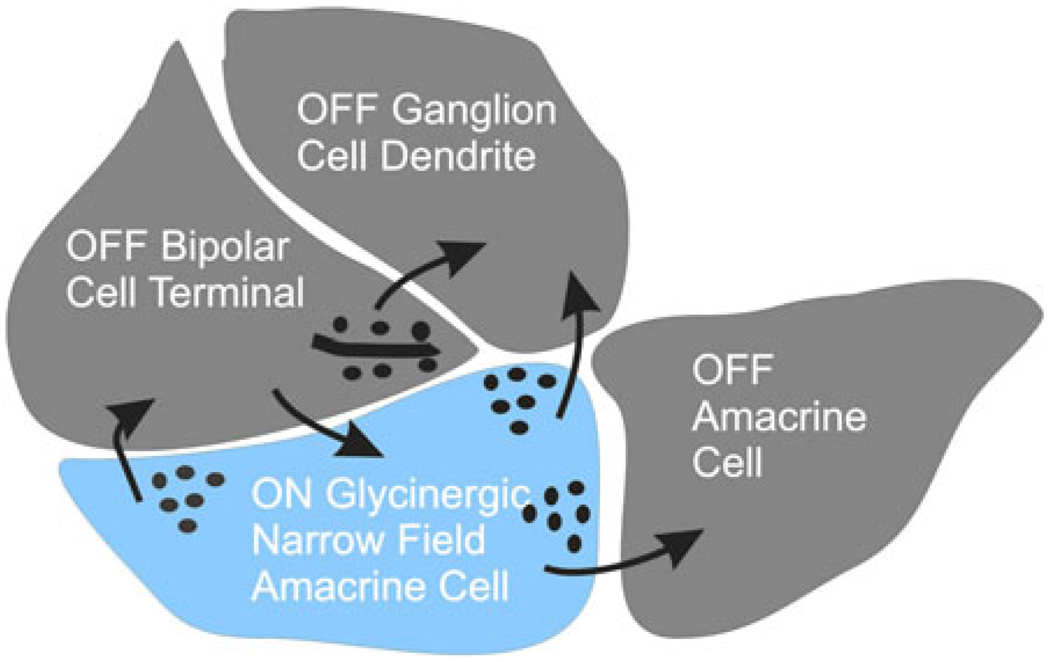
Fig. 2.
Summary sketch of electron micrograph of a synaptic terminal of an OFF bipolar cell terminal diad showing the synaptic pathways typically found in these images. OFF bipolar cell drives an OFF ganglion cell and an OFF amacrine cell. An ON amacrine cell (blue), driven by an ON bipolar cell, feeds back to the OFF bipolar cell and forward to the OFF ganglion cell. The amacrine cell also inhibits a neighboring OFF amacrine cell. A complementary set of connections would exist for the ON bipolar cell terminal. This sketch suggests all the connections that would be required for crossover inhibition to bipolar, amacrine, and ganglion cells. It is difficult to fit all of the processes around the bipolar cell ribbon in this two-dimensional representation, but all processes could be included in three dimensions.