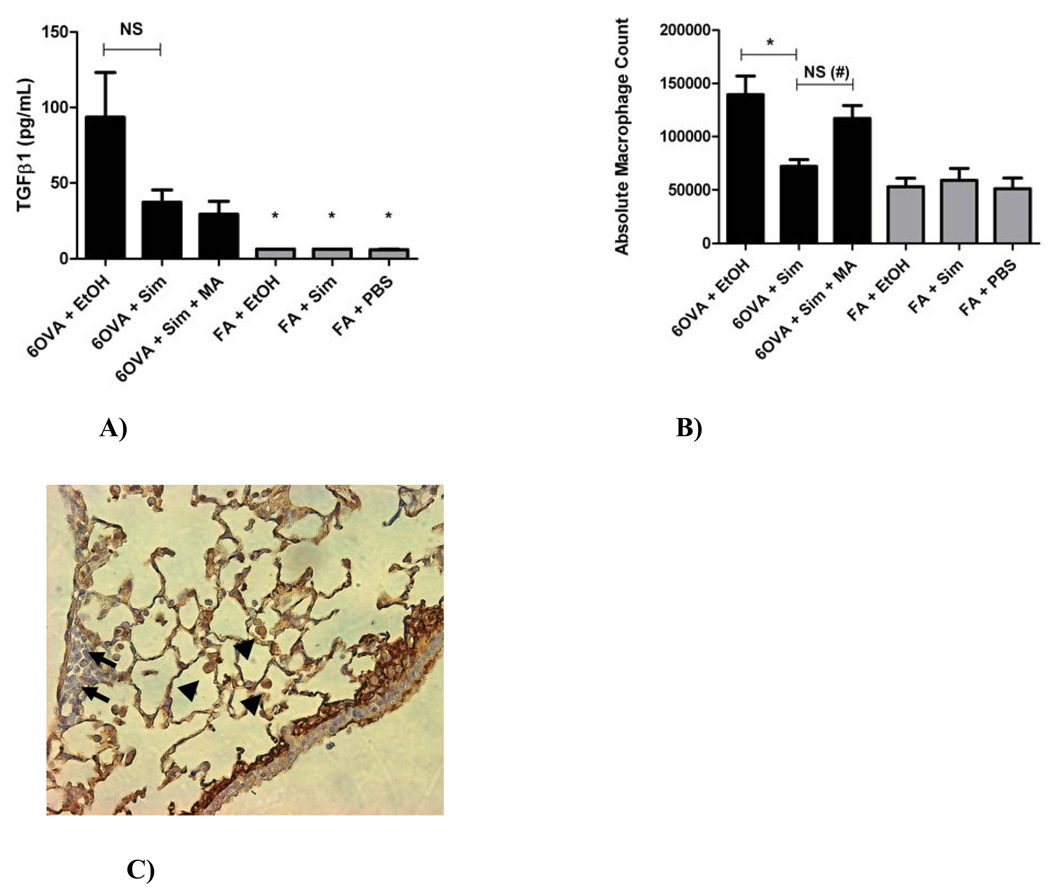
Figure 7. A) Concentration of TGFβ1 in whole lung lavage, B) Whole lung lavage Absolute Macrophage Counts, and C) TGFβ1 immunohistochemical staining of lung and inflammatory cells.
A) The group 6OVA+EtOH had significantly higher TGFβ1 concentration than any of the FA controls (*p<0.005 by 1-way ANOVA). Simvastatin (40 mg/kg) reduced TGFβ1 concentration in lung lavage by 60.4% in the OVA group (p=NS by 1-way ANOVA or t-test). Co-treatment with MA (20 mg/kg) did not reverse this inhibitory statin effect on TGFβ1. Each treatment group had between 5–6 mice.
B) Simvastatin (40 mg/kg) treatment decreased lung lavage absolute macrophage count by 48.3% (*p<0.005 by 1-way ANOVA) in OVA exposed animals. Co-treatment with MA (20 mg/kg) reversed the simvastatin inhibitory effect (p=NS by 1-way ANOVA, but #p=0.0029 by t-test). Each treatment group had between 10–17 mice.
C) By qualitative immunohistochemical assessment, macrophages appear to be the main inflammatory cells responsible for TGFβ1 production under OVA-induced allergic inflammation (image shows the 6OVA+EtOH treatment group: representative slide where TGFβ1 stains brown seen at x400 magnification). Arrows represent inflammatory cells with little-to-no staining for TGFβ1 (likely eosinophils or lymphocytes). Arrow heads represent macrophages that stain densely brown for TGFβ1.