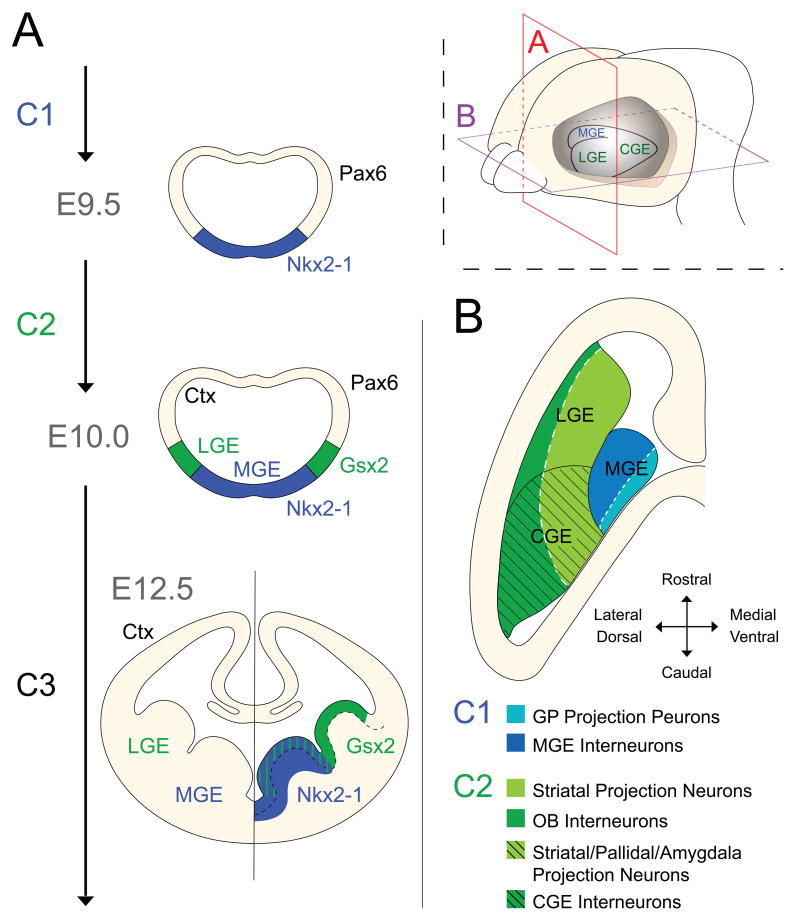
Figure 2. Early telencephalic development is characterized by the dynamic expression of distinct homeobox transcription factors that reflect the sequential appearance of the ventral eminences.
(A) At E9.5, Nkx2-1 expression appears within a ventral domain that is induced to express Shh. These events define the first temporal competence window (C1). This event defines the MGE at the molecular level and expression of Nkx2-1 persists in this region throughout development. Around E10.0 the second competence window is initiated (C2), during which the expression of Gsx2 accompanies the emergence of the more dorsally positioned lateral domain that will give rise to the LGE.
(B) After E10.0, ventral patterning is already established and Shh activity is predominantly required for proliferative control of progenitors. A horizontal view of the ventral ganglionic eminences reveals a repeated pattern in both C1 and C2-derived structures where the ventral aspect of each region gives rise to early-born projection neurons (light colors) while the more lateral/dorsal domains mainly generate later-born interneurons (darker colors).