Abstract
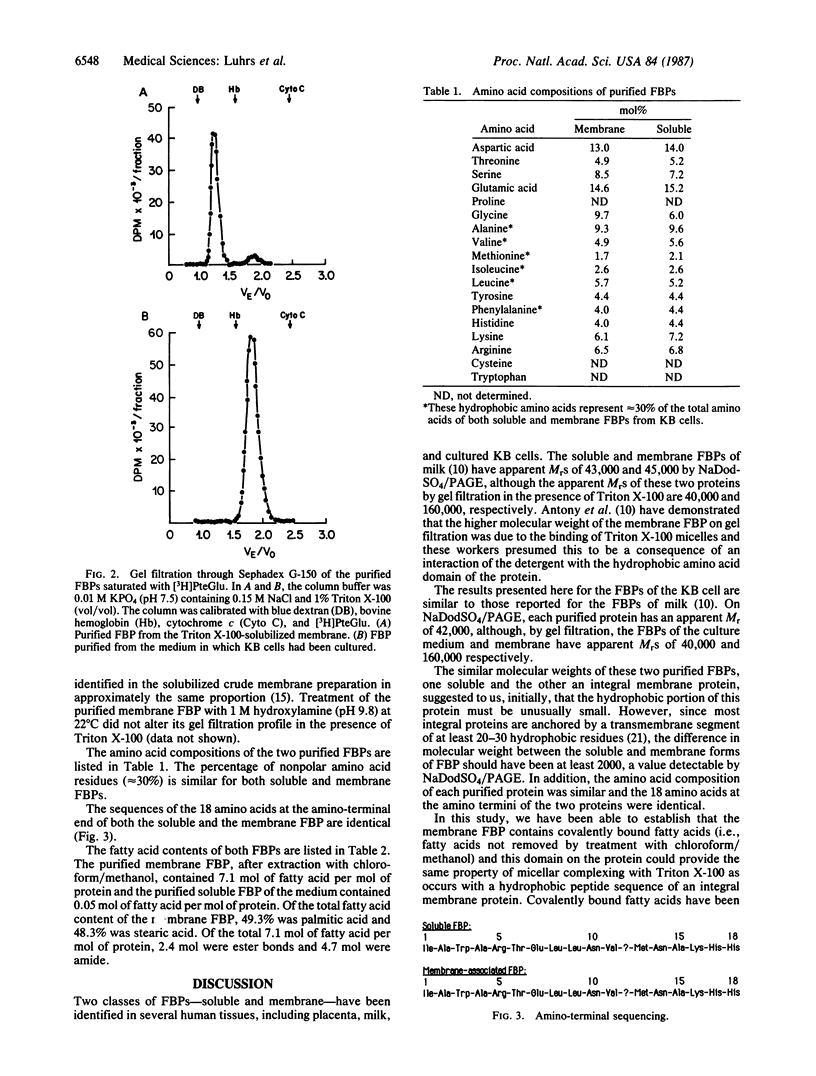
A membrane-associated folate binding protein (FBP) and a soluble FBP, which is released into the culture medium, have been purified from human KB cells using affinity chromatography. By NaDodSO4/PAGE, both proteins have an apparent Mr of approximately 42,000. However, in the presence of Triton X-100, the soluble FBP eluted from a Sephadex G-150 column with an apparent Mr of approximately 40,000 (similar to NaDodSO4/PAGE) but the membrane-associated FBP eluted with an apparent Mr of approximately 160,000, indicating that this species contains a hydrophobic domain that interacts with the detergent micelles. The amino acid compositions of both forms of FBP were similar, especially with respect to the apolar amino acids. In addition, the 18 amino acids at the amino termini of both proteins were identical. The membrane FBP, following delipidation with chloroform/methanol, contained 7.1 mol of fatty acid per mol of protein, of which 4.7 mol was amide-linked and 2.4 mol was ester-linked. The soluble FBP contained only 0.05 mol of fatty acid per mol of protein. These studies indicate that the membrane FBP of KB cells contains covalently bound fatty acids that may serve to anchor the protein in the cell membrane.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal H. C., Randle C. L., Agrawal D. In vivo acylation of rat brain myelin proteolipid protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4588–4592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antony A. C., Utley C. S., Marcell P. D., Kolhouse J. F. Isolation, characterization, and comparison of the solubilized particulate and soluble folate binding proteins from human milk. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10081–10089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antony A. C., Utley C., Van Horne K. C., Kolhouse J. F. Isolation and characterization of a folate receptor from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9684–9692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Rehn K. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):426–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changchien L. M., Craven G. R. The use of hydroxylamine cleavage to produce a fragment of ribosomal protein S4 which retains the capacity to specifically bind 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):1957–1966. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwood P. C., Kane M. A., Portillo R. M., Kolhouse J. F. The isolation, characterization, and comparison of the membrane-associated and soluble folate-binding proteins from human KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15416–15423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghitis J. The folate binding in milk. Am J Clin Nutr. 1967 Jan;20(1):1–4. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/20.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. I., Rowe P. B. Folate binding by the brush border membrane proteins of small intestinal epithelial cells. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 25;11(9):1696–1703. doi: 10.1021/bi00759a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrs C. A., Sadasivan E., da Costa M., Rothenberg S. P. The isolation and properties of multiple forms of folate binding protein in cultured KB cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Oct;250(1):94–105. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90705-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh M., Cheng Y. C. Demonstration of a high affinity folate binder in human cell membranes and its characterization in cultured human KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11312–11318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S. Covalent binding of fatty acid to the transferrin receptor in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4715–4718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg S. P. A macromolecular factor in some leukemic cells which binds folic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):428–432. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinoff M., Schreiber C., Waxman S. The isolation and characterization of the folate binding protein from goat milk. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):244–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Proteolipids. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:193–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Bracha M., Schlesinger M. J. Evidence for covalent attachment of fatty acids to Sindbis virus glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1687–1691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selhub J., Franklin W. A. The folate-binding protein of rat kidney. Purification, properties, and cellular distribution. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6601–6606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Murty V. L., Slomiany A., Zielenski J., Mandel I. D. Mucus glycoprotein of human saliva: differences in the associated and covalently bound lipids with caries. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 3;882(1):18–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Murty V. L., Takagi A., Tsukada H., Kosmala M., Slomiany A. Fatty acid acylation of salivary mucin in rat submandibular glands. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 1;242(2):402–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Takagi A., Liau Y. H., Jozwiak Z., Slomiany A. In vitro acylation of rat gastric mucus glycoprotein with [3H]palmitic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11997–12000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Brink L. Amino acid analysis of proteins and peptides at the picomole level: the fluorescamine amino acid analyzer. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):20–25. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suleiman S. A., Spector R., Cancilla P. Partial purification and characterization of a folate-binding protein from human choroid plexus. Neurochem Res. 1981 Mar;6(3):333–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00964048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Costa M., Fisher C. Immunologic heterogeneity of the folate-binding proteins from chronic myelogenous leukemia cells and myelofibrosis spleen. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Dec;98(6):956–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Costa M., Rothenberg S. P., Fischer C., Rosenberg Z. The identification and measurement of a folate-binding protein in human serum by radioimmunoassay. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jun;91(6):901–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]