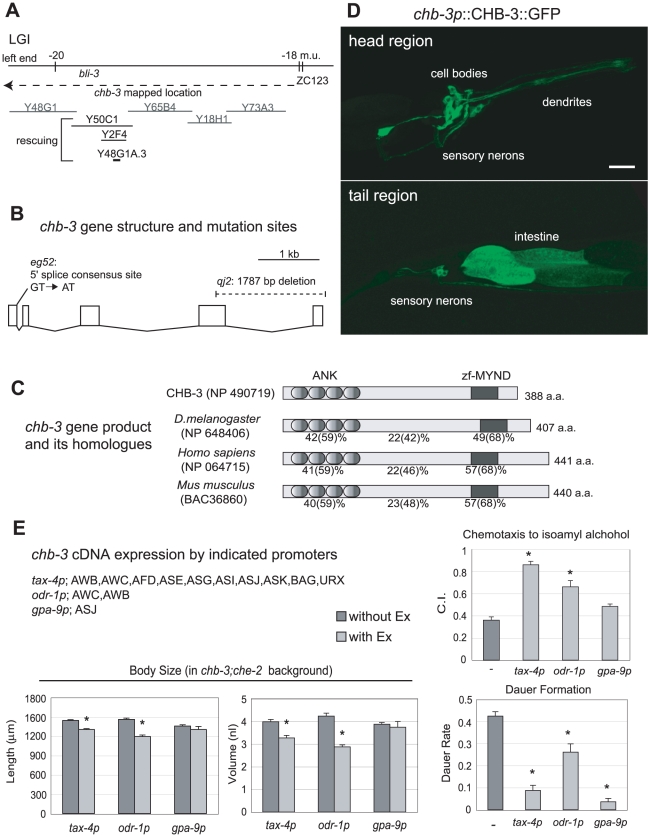
Figure 3. chb-3 encodes a novel protein with a zf-MYND motif.
(A) Genetic and physical map of the chb-3 locus. Y50C1, Y2F4 (C. elegans genomic YAC clone), and a Y48G1A.3 PCR fragment (6.5 kb) which contained the Y48G1A.3 predicted gene and 1 kb of upstream sequence, rescued the Daf-c phenotype of chb-3(eg52). The other clones are all YAC clones that failed to rescue the chb-3 phenotypes. (B) Gene structure and mutation sites of chb-3/Y48G1A.3. Exons are boxed. (C) chb-3 encodes a novel protein with four consecutive ankyrin repeats (ANK) close to the N terminus and a MYND-type Zn-finger motif (zf-MYND) close to the C terminus. Homologues from D. melanogaster (NP 648406), Homo sapiens (NP 064715), and Mus musculus (BAC36860) are included in the alignment. The amino-acid identities (and similarities in parentheses) to CHB-3 are shown for each ANK and zf-MYND domain and the region between the domains. (D) GFP expression from chb-3p::CHB-3::GFP in the head and tail regions of a wild-type animal (young adult stage). Projection of confocal microscopic sectioning images. Anterior is to the right. The scale bar represents 20 µm. (E) Phenotype rescue by chb-3 expressed under the control of the indicated sensory promoters. Sensory neurons in which each promoter drives expression are also shown. To examine rescuing of the Chb phenotype (suppression of che-2-small-body size), each construct was introduced into chb-3(eg52);che-2(e1033) animals as an extrachromosomal (Ex) array. Decrease of the size with the Ex array means rescuing of the Chb phenotype. To examine rescuing of the chemotaxis defect and Daf-c phenotype, each construct was introduced into chb-3(eg52) animals as an Ex array. Chemotaxis assays were performed with isoamyl alcohol (1/100 dilution). Animals with (light gray bars) and without (dark gray bars) the Ex array were compared. The mark (*) indicates the significant difference from control (p<0.01, t test).