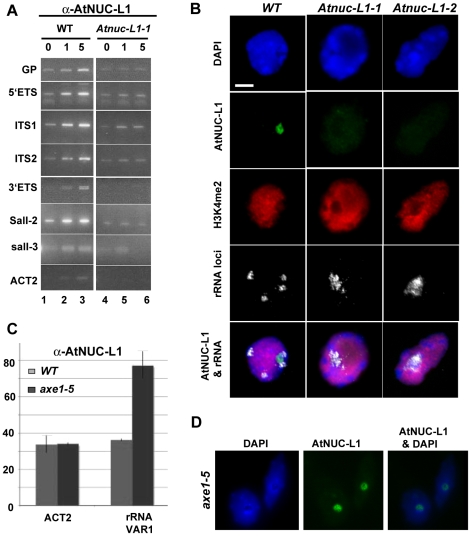
Figure 6. AtNUC-L1 binds specific rRNA gene units.
A) Chromatin isolated from WT plants was incubated either with 0, 1 or 5 µl of α-AtNUC-L1 antibody -conjugated to Protein-A (lanes 1 to 3). Immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by PCR using specific primers to detect coding 5′ETS (p22/p23), ITS1 (p24/p25), ITS2 (p26/p27) and 3′ETS (p9/p2) and non-coding GP (p20/p21), Sal1-2 (p28/p29) and Sal1-3 (p30/p31) rRNA sequences. Lanes 4–6 correspond to PCR amplification using chromatin isolated from Atnuc-L1-1 plants, which lack AtNUC-L1 protein, used as a control. Location of primers p2, p9 and p20-p31 on the rRNA gene is shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. B) Co-localization of AtNUC-L1 and rRNA genes. Counterstaining with DAPI (blue); immunodetection of AtNUC-L1 (green); immunodetection of histone H3K4 dimethylation (H3K4me2; red), FISH with a 25S rRNA probe which reveals the 45S rRNA loci (white) and the merged image (AtNUC-L1 and rRNA) on nuclei from WT, Atnuc-L1-1 and Atnuc-L1-2 mutant plants. Bar = 5 µm. C) Chromatin samples prepared from WT (grey bars) and axe1.5 mutant (black bars) plants were immunoprecipitated with α-AtNUC-L1 antibody and amplified with specific primers (p32/p33) to rRNA gene VAR1. Amplification of the ACT2 gene was performed to control ChIP and PCR reaction. D) Nucleolar localization of AtNUC-L1 in axe5-1 mutant. Counterstaining with DAPI (blue); immunodetection of AtNUC-L1 (green) and the merged image (AtNUC-L1 & DAPI) is shown.