Figure 6.
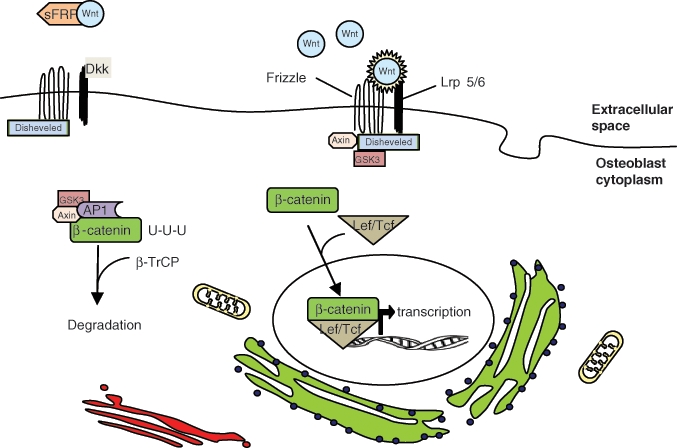
Wnt/β-catenin pathway of osteoblast differentiation. The translation of genes that stimulate osteoblast differentiation require the translocation of β-catenin from the cytoplasm to the nucleus of mesenchymal stem cells. β-catenin is targeted for degradation by the GSK3/AP1/Axin complex. Wnt binding to frizzled and Lrp 5/6 interrupts this process, allowing β-catenin to complex with Lef/Tcf. Dkk inhibits Wnt binding by interacting with Lrp 5/6. sFRP also inhibits this pathway by sequestering Wnt.
