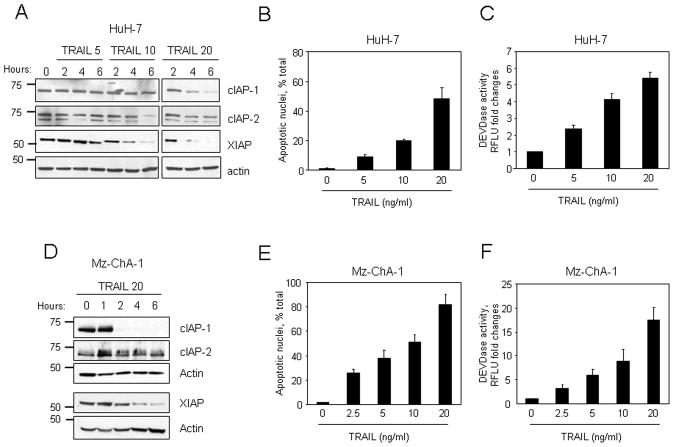
Figure 1. Degradation of cIAP-1 and XIAP is associated with TRAIL-mediated apoptosis.
(A) Hepatocellular carcinoma cells HuH-7 were treated with increasing concentrations of TRAIL (0–20 ng/ml). At the indicated time points, cell lysates were obtained and analyzed by immunoblotting for cIAP-1, cIAP-2, and XIAP. Actin was used as protein loading control. After 6 hours of treatment, apoptosis was assessed (B) by fluorescence microscopy after DAPI staining and (C) by measuring caspase 3/7 activation (DEVDase activity; relative fluorescence units - RFLU) with a fluorogenic assay, as described in Experimental Procedures. (D) Cholangiocarcinoma cells Mz-ChA-1 were treated with TRAIL (20 ng/ml). At the indicated time points, cell lysates were obtained and analyzed by immunoblotting for cIAP-1, cIAP-2, and XIAP. Actin was used as protein loading control. (E,F) Mz-ChA-1 were treated with increasing concentrations of TRAIL (0–20 ng/ml) and apoptosis was assessed by (E) fluorescence microscopy and (F) caspase 3/7 activation. Values of RFLU are expressed as fold increase over control value (untreated).