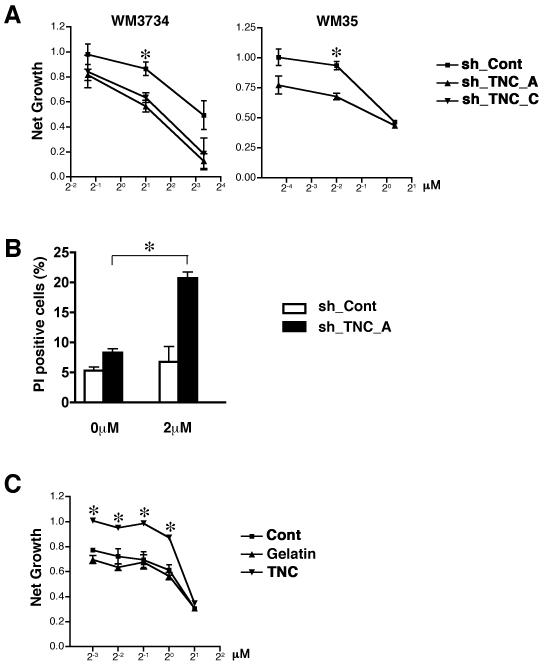
Figure 6. TNC knockdown potentiates doxorubicin response.
(A) Depletion of TNC with shRNA sensitizes melanoma cells to doxorubicin treatment, demonstrated as a shift of the sh_TNC dose response curves compared to sh_Cont cells. sh_TNC and sh_Cont cells were dissociated into single cell-suspensions in hESCM4 medium, which was conditioned for 7 days with each lentiviral infected cell line, and plated in 96-well plates at a concentration of 10,000 cells/well. Twenty-four hours later, various concentrations of doxorubicin were added. The MTS assays were performed 72 hours post drug treatment. The data were normalized to the doxorubicin-untreated control. *, p<0.05 when compared to sh_Cont cells. (B) Apoptosis assessed by propidium iodide (PI) staining of untreated and 2μM doxorubicin-treated WM3734 sh_Cont cells and sh_TNC_A cells 24 hours post-treatment. Columns indicate propidium iodide-positive apoptotic cells. Twenty-four hour treatment with 2μM doxorubicin induced apoptosis in sh_TNC_A cells but did not impair survival of sh_Cont cells. (n = 3) *, p<0.05 when compared to untreated cells. (C) Exogenous TNC increases doxorubicin resistance, demonstrated as a shift in the dose response curves. WM115 sphere cells were dissociated into single cell-suspensions in hES medium and plated in 96-well plates at a concentration of 10,000 cells/well. Cont: without additional reagent. Gelatin: with 10 μg/ml gelatin matrix. TNC: with 10 μg/ml human TNC. Twenty-four hours later, various concentrations of doxorubicin were added. The MTS assays were performed 72 hours post drug treatment. The data were normalized to the doxorubicin-untreated control. *, p<0.05 when compared to Cont cells.