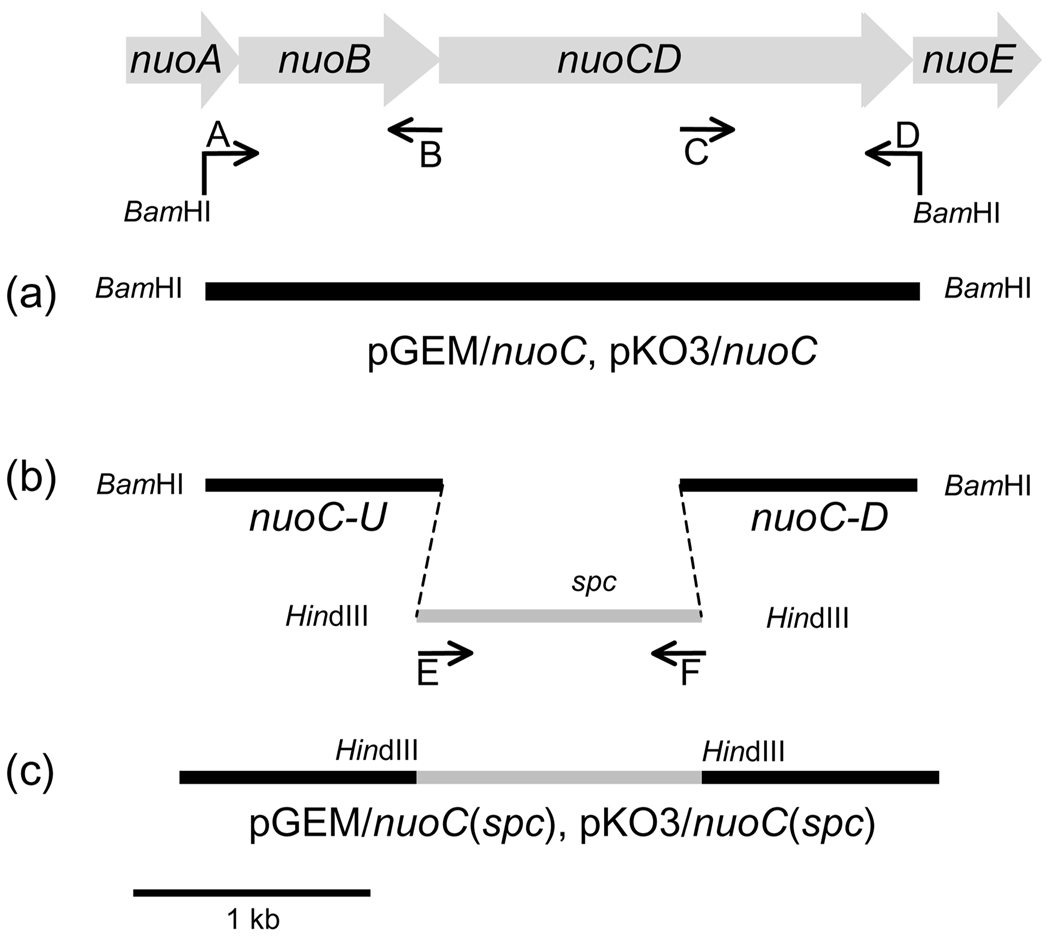
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the strategy for nuoC segment cloning, insertion of a spc cassette in the E. coli nuoCD gene and the construction of site-specific NuoC segment mutants. In this work, we selected the part of nuoCD gene that codifies the homologous segment of the Nqo5 from T. thermophilus (NuoC). Arrows indicate the primers used in this study. (a) Amplified product nuoC+1 kb upstream +1 kb downstream (NuoC) was cloned in pGEM-T Easy vector and subcloned into the vector pKO3 resulting in plasmids named pGEM/nuoC and pKO3/nuoC, respectively. (b) The spectinomycin-encoding gene (spc) was obtained by using the primers E and F, both containing the HindIII restriction site. (c) spc was cloned in pGEM-T Easy vector and inserted between the fragments nuoC-U and nuoC-D utilizing the HindIII restriction sites and finally assembled in the pKO3 vector (pKO3/nuoC (spc)) with the help of BamHI restriction sites.