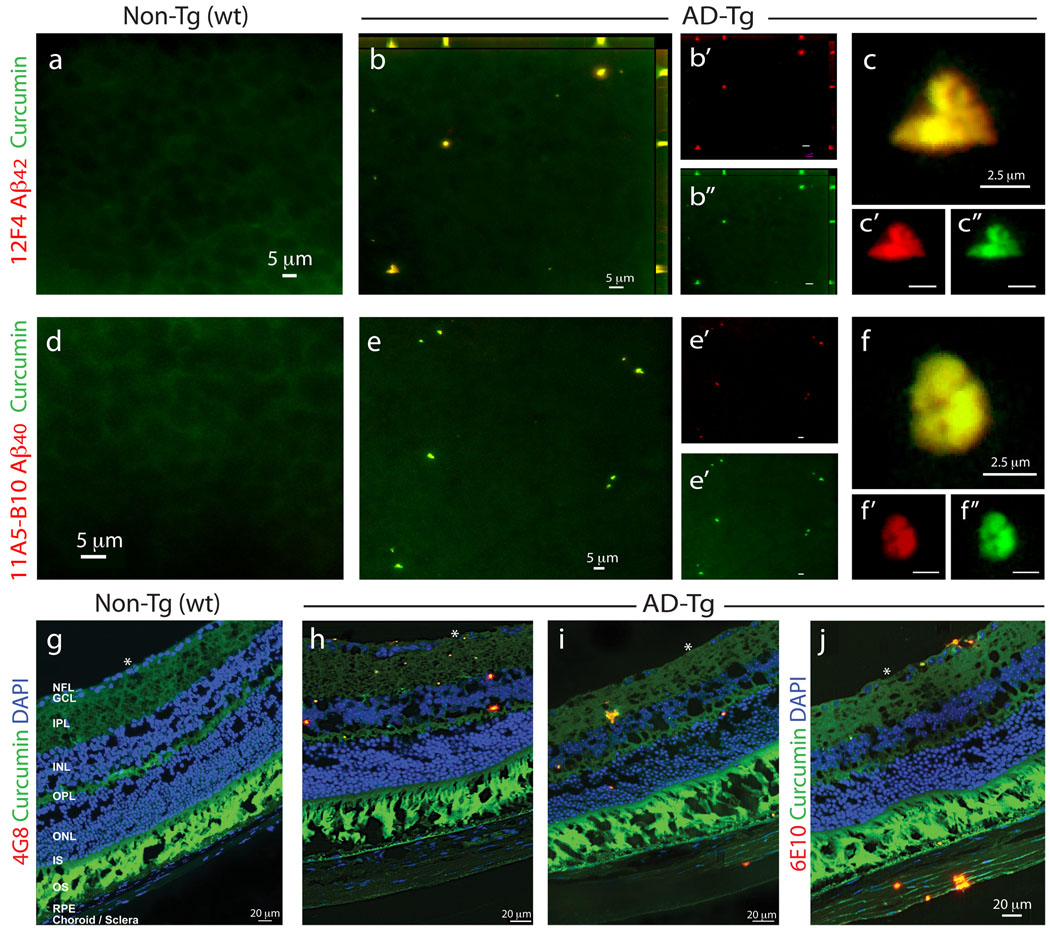
Figure 1.
Detection of retinal Aβ plaques in AD-Tg mice by ex vivo curcumin labeling. Whole-mount retinas and whole-eye sagittal cryosections from 10-month-old non-Tg (wt) and AD-Tg mice stained with various anti-human Aβ mAbs (12F4, 11A5-B10, 4G8 and 6E10; secondary Ab-Cy5 conjugate; red color) and curcumin (green color). Double-labeled Aβ plaques appear in yellow color. (a–c) Representative images of whole-mount retinas double-stained with curcumin and Aβ42 mAb (12F4; specific to the C-terminal sequence ending at aa 42). (a) No retinal Aβ plaques were detected in wt mice, whereas (b) they were found in AD-Tg mice; here and below, whenever z-axis projection images are presented, the axes ZY and ZX are shown on the top and right side of the image. (c) Specific staining patterns of Aβ42-containing retinal plaques at a higher magnification; (b’–c”) Separate channels for each staining; (d–f) Whole-mount retinas double-stained with anti-human Aβ40 mAb (11A5-B10; specific to the C-terminal sequence ending at aa 40) and curcumin. (d) No detection of Aβ plaques in wt mice. (e) Specific Aβ plaques were found in AD-Tg mice. (f) Higher magnification image demonstrating Aβ40-containing plaques and their specific staining pattern. (e’–f”) separate channels. (g–j) Whole-eye cross-sections stained with anti-Aβ mAbs (4G8 or 6E10), curcumin and DAPI nuclei staining. (g) No evidence for double-positive curcumin and anti-human Aβ plaques in wt mice. (h–j) Curcumin-positive Aβ plaques co-labeled with 4G8 or 6E10 were identified in various retinal layers, including the GCL-ganglion cell layer, IPL-inner plexiform layer, INL-inner plexiform layer, OPL-outer plexiform layer and ONL-outer Nuclear Layer. (i,j) Aβ plaques were also detected in the sclera. White Asterisks indicate DAPI nuclei staining in the GCL: undamaged in wt retinas and deficient in retinas from AD-Tg mice.