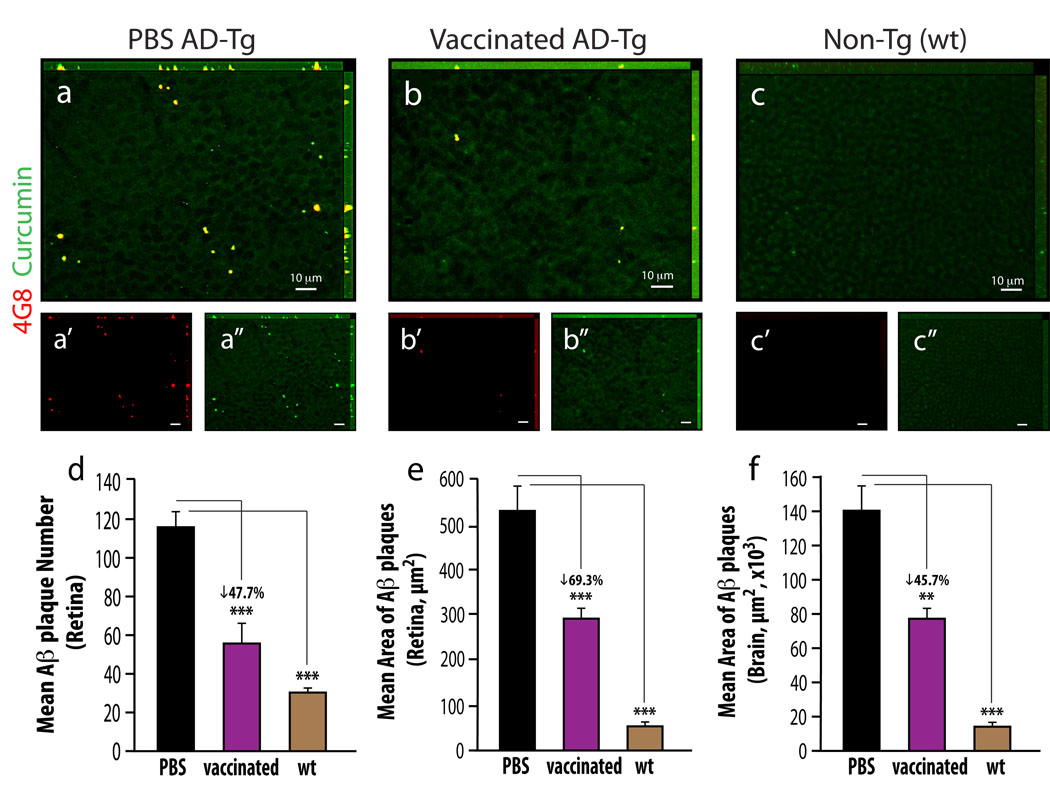
Figure 3.
Reduced Aβ-plaque burden in retinas from AD-Tg mice following MOG45D-loaded dendritic cells immunization. (a–c) Representative z-axis projection images of whole-mount retinas from (a) PBS-treated control and (b) MOG45D-immunized AD-Tg mice, and from (c) non-Tg (wt) mouse, stained ex vivo with curcumin and anti-human Aβ mAb (4G8; followed by secondary Ab-Cy5 conjugate). (d,e) Following MOG45D-loaded DCs immunization, a significant reduction in mean curcumin-positive plaque number and area was observed in retinas from immunized AD-Tg mice as compared to PBS-treated controls and non-Tg (wt) mice. (f) A significant decrease in total area covered by plaques was detected in brain hippocampus and cortex from the same mice following the immunotherapy. Curcumin staining revealed the same decrease in plaque burden following immunization in the retina and in the brain, while Aβ mAbs confirmed its specificity to Aβ, suggesting that curcumin is a suitable dye for monitoring Aβ plaques. Error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: *** P<0.0001; ** P<0.005, analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison post-test.