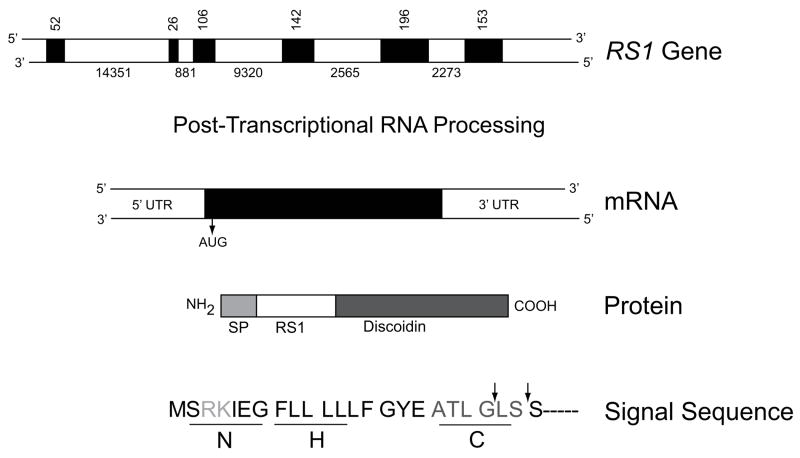
Figure 1.
Schematic structure of the RS1 gene, mRNA, and protein products. RS1 is encoded on the minus strand of the X chromosome at Xp22.2–p22.1 covering 32.43 kb from 18600150 to 18567724. Exons are indicated by filled boxes, with numbers indicating the size of the exons and introns in nucleotides. The primary RNA transcript encoding both exons and introns undergoes post-transcriptional RNA splicing to remove introns and generate mRNA (NM_000330.3*) which is translated into a 224 amino-acid protein (NP_000321.1). The functional domains of RS1 are 1) a signal peptide (SP), 2) RS1, and 3) the discoidin domains. The signal sequence guides the translocation of nascent RS1 from the endoplasmic reticulum (the site of synthesis) to external leaflet of the plasma membrane, during which signal sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase to generate mature protein with characteristic RS1 and a highly conserved discoidin domain. The different subdomains of RS1 signal sequence are 1) the positively charged N region at the amino terminal end which mediates translocation, 2) the hydrophobic core (H) required for targeting and membrane insertion and 3) a polar “C” region that determines the site of recognition and cleavage by signal peptidase. The arrows indicate the sites at which the signal peptide is cleaved. *The numbering follows GenBank NCBI Reference Sequence: NM_000330.3. Nucleotide 1 is A of the ATG initiation codon (CDS 36–710).