Figure 6.
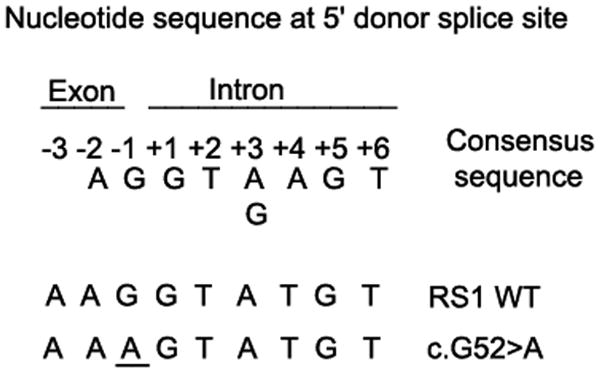
Sequence of eight highly conserved nucleotides at the boundary between an exon and an intron: the 5′ donor splice site (5′ ss) of eukaryotic mRNAs (Shapiro and Senapathy, 1987). Also shown are the sequences at the boundary between exon 1 and intron 1 in RS1 WT and c52 G>A mutant. Splicing is catalyzed by spliceosome, an RNA/protein complex consisting of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs) and SR family of splicing proteins (splicing factors with one or more RNA-recognition motif) through RNA–RNA and protein–protein interactions. snRNPs are composed of snRNAs (U1, U2, U4N6, and U5) each associated with 8 sm proteins. These snRNPs assemble on the conserved sequence motifs at three sites: U1 at exon–intron junction (5′ splice site), U2AF at intron–exon junction (3′ splice site) and U2 at branch point located 18–40 nucleotides upstream of the 3′ splice site.
