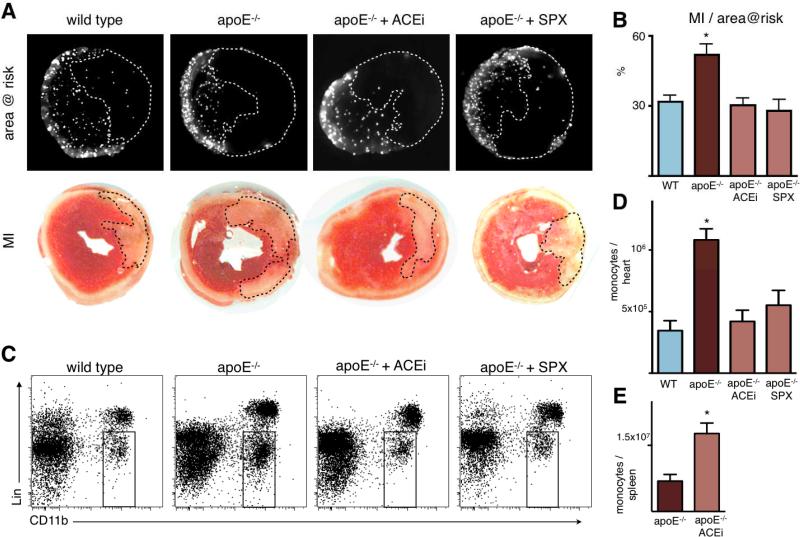
Figure 8. Ischemia reperfusion injury is enhanced in apoE-/- mice with inflammatory atherosclerosis, and attenuated by Enalapril and splenectomy.
A: Fluorescence reflectance images display the area at risk, which is void of microspheres injected during ischemia. Lower panel shows TTC staining of the same myocardial short axis slice.
B: Quantification of ischemia reperfusion injury as a percentage of the area at risk. Mean ± SEM; * p < 0.05 versus all other groups.
C: Representative flow cytometry dot plots of heart tissue from apoE-/- mice 1 day after ischemia. The gate shows CD11b positive lineage negative monocytes and macrophages.
D: Quantification of CD11b positive lineage negative monocytes/macrophages. * p < 0.05 versus all other groups.
E: Flow cytometric quantification of splenic monocytes 24 hours after ischemia in apoE-/- mice with and without Enalapril treatment (ACEi). Mean ± SEM; * p < 0.05.