FIGURE 3.
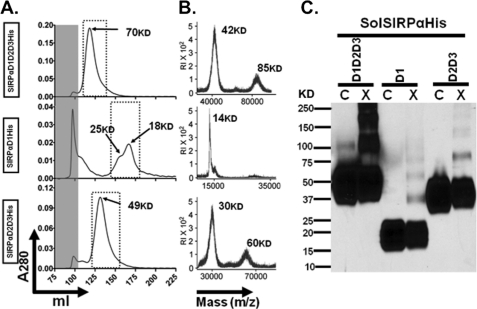
The IgC folds of SIRPα ectodomains are critical for dimerization of SIRPα. Soluble full-length and truncated ectodomains tagged with 10 histidines were produced in HEK293T cells and purified using nickel-NTA columns. A, gel filtration chromatography analysis demonstrating that full-length SIRPα ectodomain (SIRPαD1D2D3His) with a predicted molecular weight of 38,000 eluted as a single peak with an apparent molecular weight of 70,000. SIRPαD1His (membrane-distal IgV fold) has a predicted molecular weight of 16,000 but eluted as two major peaks with apparent molecular weights of 25,000 and 18,000. SIRPαD2D3His (membrane-proximal IgC folds) has a predicted molecular weight of 26,000 but eluted as a single peak with an apparent molecular weight of 49,000. Void volume is indicated by the gray-shaded area. B, MALDI-TOF analysis of the eluted recombinant SIRP proteins. As can be seen, SIRPαD1D2D3His consisted of monomers at 42 kDa and dimers at 85 kDa, and SIRPαD2D3His consisted of monomers at 30 kDa and dimers at 60 kDa. In contrast, SIRPαD1His consisted of only monomers at 16 kDa. C, immunoblot analysis of purified SIRPα proteins using rabbit antiserum against the full-length SIRPα ectodomain, confirming the presence of noncovalently linked dimers after cross-linking with BS3. Results are representative of one of five independent experiments. C, control; X, cross-linked.