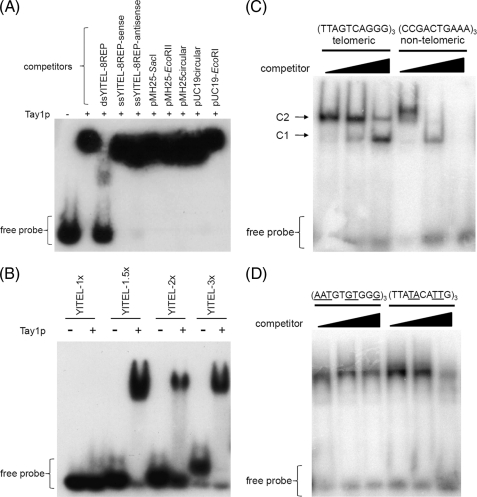
FIGURE 3.
DNA binding properties of Tay1 analyzed by EMSA. A, shown is EMSA analysis using radiolabeled YlTEL (50-bp EcoRI fragment of pMH25) as a probe. The DNA competitors indicated above the lanes were used at a 1000-fold excess over the YlTEL probe. B, Tay1p is able to bind dsDNA probes carrying ≥1.5 telomeric repeats. C, EMSA analysis using radiolabeled dsDNA oligonucleotides containing three telomeric repeats (telomeric' YlTEL_EMSA-1) and three non-telomeric repeats (nontelomeric YlTEL_EMSA-C), respectively. 100, 300, and 500 ng of poly(dI-dC) DNA were used as competitor DNA. The two bands (C1 and C2) most likely represent complexes containing one and two Tay1 protein molecules, respectively. D, shown is an EMSA analysis of Tay1p binding to radiolabeled mutated telomeric probes containing either conserved GT and GG dinucleotides with other residues of the telomeric repeat mutated ((AATGTGTGGG)3; YlTEL_EMSA-M5) or vice versa ((TTATACATTG)3; YlTEL_EMSA-M6). Mutated residues are underlined. 300, 500, and 1000 ng of linearized pUC19 were used as a competitor. In all EMSA experiments the dsDNA probes were prepared by annealing ss oligonucleotides as described under “Experimental Procedures.”