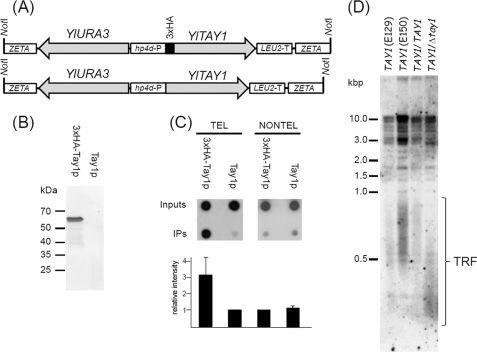
FIGURE 7.
Tay1p binds telomeres of Y. lipolytica in vivo. A, YlTAY1 was cloned with (3×HA-Tay1p) or without (Tay1p) the 3×HA epitope into pINA1312 plasmid vector as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The NotI fragment of the plasmid carrying YlTAY1 and YlURA3 (selection marker) flanked by ZETA sequences facilitating integration into the Y. lipolytica genomic DNA was gel-isolated and transformed into the Y. lipolytica strain PO1h. B, expression of 3×HA-Tay1p was tested by immunoblot analysis of protein extracts prepared from cells transformed with DNA carrying the gene encoding YlTay1p with or without 3×HA epitope. C, ChIP analysis of association of Tay1p with telomeric sequences is shown. Cells expressing 3×HA-Tay1p or Tay1p lacking the epitope were treated with formaldehyde, and 3×HA-Tay1p was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HA antibodies as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The presence of telomeric DNA in immunoprecipitates (IP) was detected by dot-blot analysis using radioactively labeled YlTEL-4x oligonucleotide containing four Y. lipolytica telomeric repeats (TEL) or a mixture of oligonucleotides (YARLI-T1-4x, YARLI-T2-4x, and YARLI-T3-4x) derived from three arrays of non-telomeric tandem repeats (NONTEL). The relative intensity of the spots was determined using ImageJ software (rsb.info.nih.gov). The graph represents results of three independent experiments. D, measurement of TRFs in haploid strains (E129, E150), parental diploid strain (E129xE150; TAY1/TAY1), and heterozygous strain lacking one functional copy of TAY1 gene (TAY1/Δtay1) are shown. In contrast to the lengths of TRFs typical for parental wild-type strains (500–1000 bp), the heterozygote exhibits substantially shorter TRFs (300–500 bp).