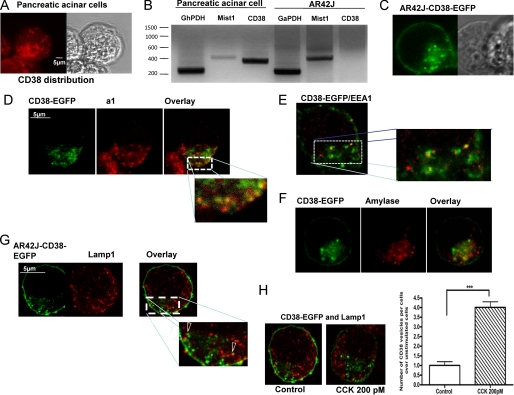
FIGURE 3.
Subcellular distribution of CD38 in pancreatic acinar and AR42J cells. A, confocal microscopy reveals endogenous CD38 distribution in primary pancreatic acinar cells. B, CD38 is not present at the mRNA levels in AR42J cells, whereas CD38 mRNA was detected in normal pancreatic acinar cells. Mist 1 is a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor that is highly expressed in the adult pancreas (B). C, transiently expressed CD38-EGFP construct in AR42J cells. D, co-immunostaining CD38 and a1 subunit of the vacuolar V-H+-ATPase, an endolysosomal marker. E, shown is a co-localization of CD38-containing vesicles with the early endosomal marker, EEA1. F, shown is a co-immunostaining of CD38-containing vesicles with amylase containing granules at the secretory pole (G) lysosomes, marked with LAMP1 staining appose CD38-containing vesicles but do not co-localize. H, application of CCK (200 pm for 30 s) sharply increases the number of CD38-expressing vesicles in AR42J-CD38 cells. However, even after CCK stimulation, co-immunostaining of CD38 and Lamp1 indicates that CD38-containing vesicles are distinct from lysosomes.