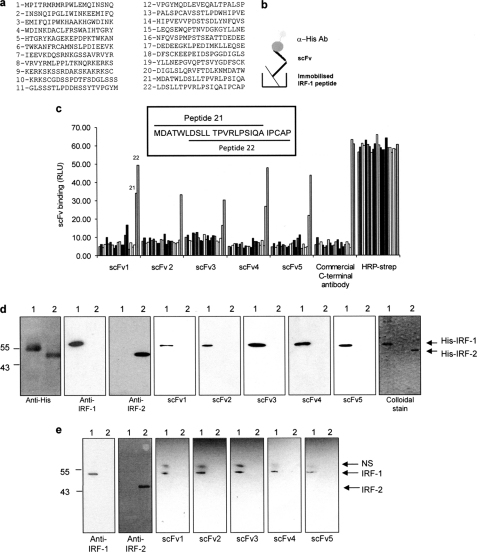
FIGURE 2.
scFv binding to denatured IRF-1. a, list of overlapping peptides covering the complete sequence of IRF-1 used in c. Peptide 22 was used for phage screening. b, schematic of scFv binding to biotinylated peptides in a peptide binding assay. c, immobilized overlapping peptides (peptides 1–22; given in a) were incubated with each scFv (1 μg/ml). Following extensive washing, scFv binding was detected with an anti-His monoclonal antibody and enhanced chemiluminescence. A commercial anti-IRF-1 C-terminal peptide antibody was used as a control, and peptide normalization was demonstrated using HRP-streptavidin to detect the biotin moiety. The sequences of two overlapping peptides (21 and 22) are shown in the inset. d, purified His-IRF-1 (lane 1) and His-IRF-2 (lane 2) (0.3 μg/lane) were analyzed on a 12% SDS-PAGE/immunoblot and probed with anti-His, anti-IRF-1, anti-IRF-2 and the scFv nanobodies (1 μg/ml). scFv binding was detected using anti-GST monoclonal antibody, and enhanced chemiluminescence. A colloidal stain shows the purity of His-IRF-1 and His-IRF-2. e, lysates from HeLa cells transfected with 1 μg of pcDNA3 IRF-1 (lane 1) or pcDNA3 IRF-2 (lane 2) were analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE/immunoblot and probed with the antibodies listed in d with the exception of the anti-His antibody. NS, nonspecific band detected by the anti-GST antibody. The data are representative of at least two independent experiments.