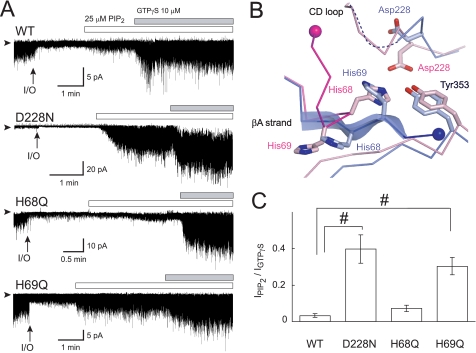
FIGURE 3.
Effects of amino acid substitution on PIP2-induced channel activation. A, effects of PIP2 and GTPγS on currents of Kir3.2 WT, D228N, H68Q, and H69Q mutant channels. The channels were expressed in HEK cells and examined in inside-out membrane patches. Experiments were conducted in symmetric 135 mm K+ solutions with a holding potential of −100 mV. The protocol of perfusion of substances to the intracellular side of the patch membrane is indicated above the current traces. Arrowheads indicate the zero current levels, and arrows (I/O) indicate the time point when the patch was excised. B, comparison of residues involved in the interaction between the N terminus and the CD loop. The Cα traces involved in this interaction in the Na+-plus and Na+-free Kir3.2 structures are colored blue and pink, respectively. The residues critical for the interaction are depicted as stick models. The ends of the N terminus connecting to the slide helix are shown as spheres. C, the summary of PIP2-induced current amplitudes of WT (n = 5), D228N (n = 5), H68Q (n = 7), and H69Q mutants (n = 9) channels (means ± S.E.), which were normalized against that activated by 10 μm GTPγS (#, p < 0.01).