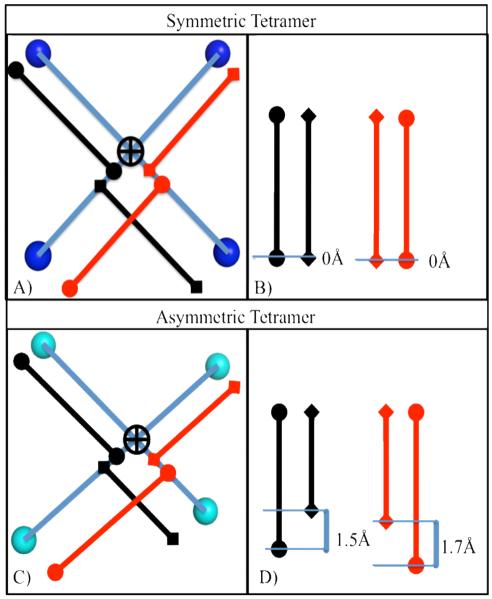
Figure 4.
Schematic of mobility assessment algorithm for any 2D projection of a D4h set of spheres. (A) A perfectly symmetric tetramer, showing lines connecting the opposing balls (blue), the calculated intersection (black cross), and the respective two sets of line segments (black and red). (B) The length of the sets of line segments is tabulated and they are subtracted to estimate the motility, which is zero for the perfectly symmetric tetramer. C) An asymmetric tetramer, showing lines connecting the opposing balls (green), the calculated intersection (black cross), and the respective two sets of lines segments (black and red). D) Substantial deviation from perfect symmetry is shown in this projection due to the magnitude of inequality in the respective vector sets.