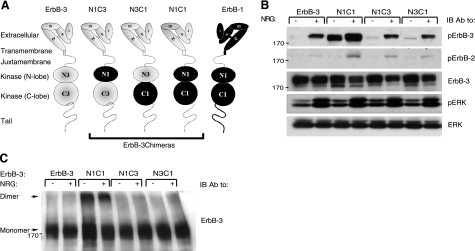
Figure 1.
The N1C1 chimera is constitutively phosphorylated and dimerized. A) Schemes present domain organizations of wild-type ErbB-3 (gray), ErbB-1/EGFR (black), and their chimeric derivatives. N denotes the N lobe and C denotes the C lobe of the respective tyrosine kinase domain. The 4 subdomains of the extracellular regions are denoted I–IV. Dashed line represents the cytoplasmic tail of ErbB-3; solid line represents tail of ErbB-1. Three chimeras are outlined. B) Plasmids encoding ErbB-3 (wild type), N1C1, N1C3, or N3C1 were cotransfected with a plasmid encoding a kinase-dead mutant of ErbB-2 (KD-B2) into CHO cells. After 48 h, cells were stimulated for 5 min without or with NRG (25 ng/ml). Thereafter, cells were detached using a scraper and lysed. Lysates were cleared by centrifugation, resolved by electrophoresis, and then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. Anti-phopsho-ErbB-3 and anti-phospo-ErbB-2 antibodies were used to monitor receptor phosphorylation, whereas an anti-phospho-ERK antibody was used to assess the activation of ERK. An anti-ErbB-3 antibody was used to verify ectopic expression levels, and an antibody against ERK was utilized to verify equal loading. C) Plasmids encoding wild-type ErbB-3, N1C1, N1C3, or N3C1 were cotransfected into CHO cells together with a plasmid encoding the KD-B2 molecule. Cells were stimulated as in B and then washed with cold PBS. Thereafter, cells were detached using a scraper and extracted for 20 min at 4°C in lysis buffer containing the cross-linker BS3 (2 mM). The reaction was terminated by the addition of glycine (20 mM). Lysates were processed as in B. Dimers and monomers (arrows) were detected using an anti-ErbB-3 antibody.