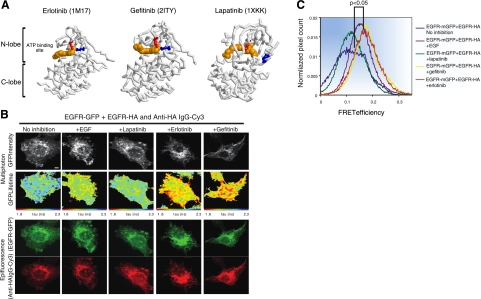
Figure 5.
FRET/FLIM analysis reveals that erlotinib and gefitinib, but not lapatinib, induce dimerization of ErbB-1/EGFR. A) Three-dimensional structures of the kinase domain of ErbB-1 bound to erlotinib, gefitinib, or lapatinib. Erlotinib (PDB 1M17)- and gefitinib (PDB 2ITY)-bound kinase is active (note salt bridge formed between K721, in red, and E738, in blue, which are in proximity), whereas the lapatinib-bound form (PDB 1XKK) is inactive (K721 and E738 are distant). Structural components of the kinase (N lobe, C lobe, and ATP-binding site) are labeled. B) MCF-7 cells were transfected with vectors encoding EGFR-mGFP and EGFR-HA. Cells were incubated for 24 h, serum starved for 1 h, and stimulated with EGF (50 ng/ml) for 1 h. Alternatively, cells were treated with lapatinib, gefitinib, or erlotinib as indicated (10 μM) for 1 h, prior to fixation and staining with an anti-HA antibody conjugated to Cy-3. Scale bars = 5 μm. C) Cumulative histogram of FRET efficiency between EGFR-mGFP and HA-Cy3 (bound to EGFR-HA) calculated with the following equation in each pixel and averaged per cell: FRET efficiency = 1 tau (da)/tau (control), where tau (da) is the lifetime displayed by cells coexpressing both EGFR-mGFP and EGFR-HA stained with an anti-HA IgG-Cy3, whereas tau (control) is the mean EGFR-mGFP lifetime measurement in the absence of the Cy3 acceptor. Data were obtained from 4–11 cells/treatment group and are representative of 2 independent experiments. Values of P are 0.003 and 0.025, respectively, for comparisons between untreated cells and cells treated with gefitinib or lapatinib, respectively, according to analysis of variance with post hoc testing using Tukey's honest significant test.