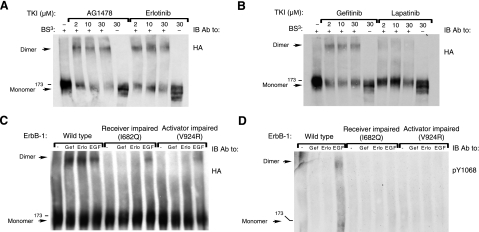
Figure 6.
Cross-linking analysis reveals that AG1478, erlotinib, and gefitinib, but not lapatinib, induce dimerization of ErbB-1/EGFR. A, B) CHO cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding HA-tagged ErbB-1, and 48 h later, they were incubated for 60 min at 37°C with increasing concentrations of AG1478, erlotinib, gefitinib, or lapatinib, as indicated. Cells were then washed with cold PBS and harvested in lysis buffer containing the BS3 cross-linker. After 20 min at 4°C, the cross-linking reaction was terminated by the addition of glycine (20 mM). Thereafter, lysates were cleared by centrifugation, resolved by electrophoresis, and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. Dimers were detected using an antibody against the HA tag. C, D) Cells were transfected with plasmids encoding wild-type ErbB-1/EGFR, a receiver-impaired (I682Q) mutant, or an activator-impaired (V924R) mutant of ErbB-1/EGFR. After 48 h, cells were treated with or without gefitinib (10 μM), erlotinib (10 μM), or EGF (50 ng/ml) and then lysed and cross-linked as in A. Dimers and monomers were detected using an antibody against the HA tag, and tyrosine phosphorylation was monitored using an antibody to the phosphorylated form of EGFR's tyrosine 1068.