Fig. 1.
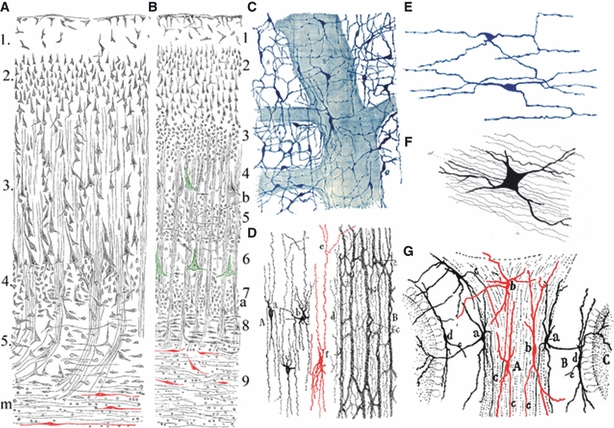
Meynert was first to describe neurons in the adult subcortical white matter, and Ramón y Cajal introduced the term interstitial cells in neurohistology. Neurons (red) in the subcortical white matter of the human brain (A – frontal, B – primary visual cortex) were first described by Theodor Meynert in 1867 (here reproduced from Meynert, 1884, pp. 53 and 63). However, the term interstitial cells was initially (1891–93) applied by Ramón y Cajal to describe a special type of visceral sympathetic neurons in glands and the enteric system of the gut (C–,E – here reproduced from Ramón y Cajal, 1911, pp. 924–927; (C,D) interstitial cells in Auerbach's plexus and muscular layer of the rabbit intestine, stained by methylene blue; (E) interstitial cells among muscle fibres of the guinea-pig intestine, stained by rapid Golgi method). Cajal in 1896 also described neurons in the cerebellar white matter as interstitial cells (G –Ramón y Cajal, 1896, p. 24, fig. 5b), but it should be noted that these cells were first described by Gustav Retzius (F –Retzius, 1892, fig. 4 of Plate XIX). For details, see text.
