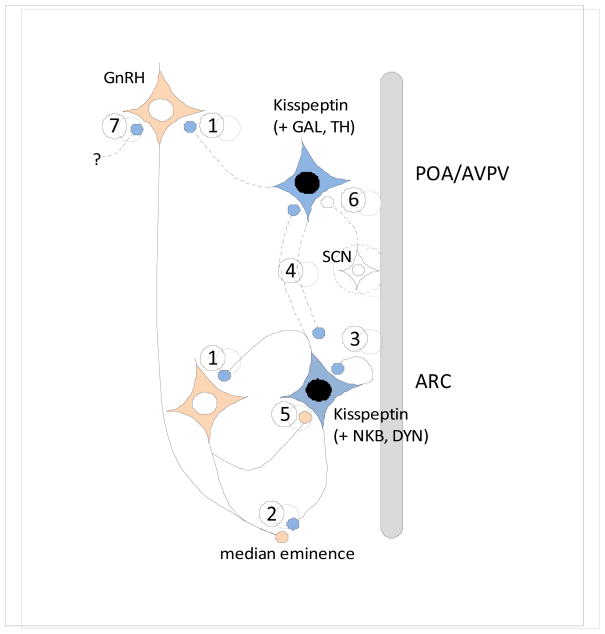
Fig. 2. Schematic horizontal section (top=rostral, bottom=caudal) showing the POA/AVPV and ARC kisspeptin populations in the mammalian hypothalamus, and their potential sites of interactions with GnRH neurons.
Virtually all ARC kisspeptin neurons co-express neurokinin B and dynorphin (Goodman et al., 2007; Navarro et al., 2009; Wakabayashi et al., 2010), while subsets of AVPV kisspeptin neurons in the preoptic region express either galanin (Vida et al., 2009) or tyrosine hydroxylase (Kauffman et al., 2007b). Connections (solid lines, published data; dotted lines, unpublished data) and sites of interactions between kisspeptin and GnRH systems include: 1) Direct projections from ARC and AVPV kisspeptin cells onto GnRH cell bodies (Clarkson and Herbison, 2006; Kinoshita et al., 2005; Krajewski et al., 2005; Lehman et al., 2010; Ramaswamy et al., 2008; Smith et al., 2008); 2) Inputs from ARC kisspeptin cells onto GnRH terminals in the median eminence (Burke, 2006; Krajewski et al., 2005; Lehman et al., 2010; Ramaswamy et al., 2008); 3) reciprocal connections among ARC kisspeptin cells that could be from the same or adjacent neurons (Burke, 2006; Foradori et al., 2002; Krajewski et al., 2010; Wakabayashi et al., 2010); 4) Projections from ARC kisspeptin neurons to POA kisspeptin cells in the sheep (Lehman, unpublished), and from AVPV kisspeptin neurons back to the ARC (Yeo and Herbison, 2009); and 5) projections from GnRH neurons back onto ARC kisspeptin cells (Ramaswamy et al., 2008). In addition, afferents to POA/AVPV kisspeptin cells from the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) are indicated (6) (Vida et al., 2010), as well as the possibility that kisspeptin inputs to GnRH neurons in the POA or MBH may arise from other populations such as the DMH, BNST or medial amygdala (7).