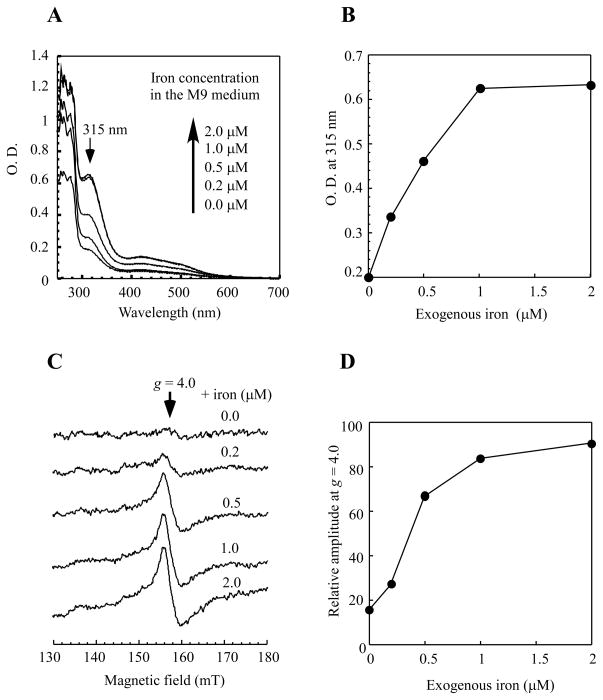
Figure 2. Relative iron binding activity of IscA in E. coli cells under aerobic conditions.
A) UV-visible absorption spectra of recombinant IscA purified from E. coli cells grown aerobically in the M9 minimal medium supplemented with ferric citrate (0.0, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0μM). The protein concentration of purified IscA was about 250 μM. B) The apparent iron binding activity of IscA in E. coli cells. The amplitude of the absorption peak at 315 nm of purified IscA in A) was plotted as a function of the exogenous iron concentration supplemented in the M9 minimal medium. C) The EPR spectra of the E. coli cells treated with an iron indicator desferrioxamine. The E. coli cells grown in the M9 minimal medium supplemented with ferric citrate (0.0, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 μM) were subject to the intracellular iron content measurements using the iron indicator desferrioxamine as described in the Experimental section. The amplitude of the EPR signal at g = 4.0 reflects the relative intracellular iron concentration in E. coli cells. D) The amplitudes of the EPR signal at g = 4.0 in C) were plotted as a function of the exogenous iron concentration supplemented in the M9 minimal medium. The data are representatives from three independent experiments.