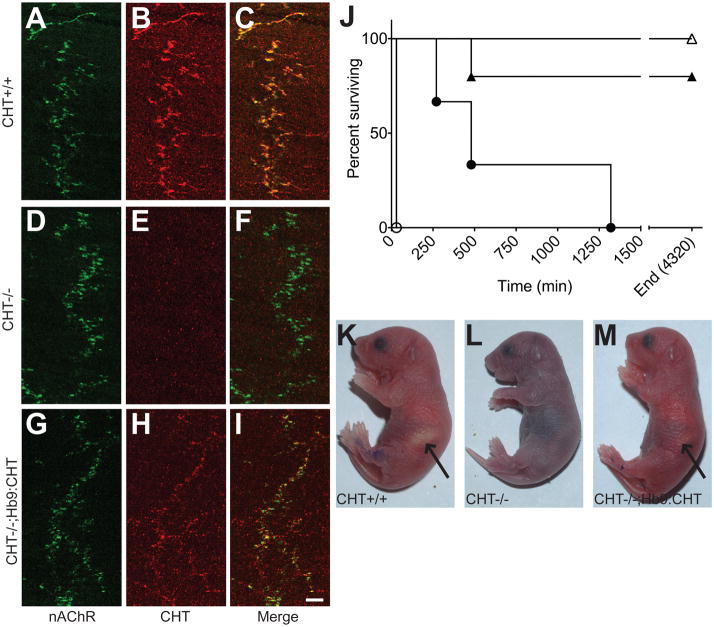
Fig. 2.
Expression and function of CHT from HB9:CHT demonstrated in Hb9:CHT;CHT−/− neonatal mice: (A–I) Immunostaining for alpha Bungarotoxin and neurofilaments (A, D, G) and CHT (B, E, H) with the merged images (C, F, I) in CHT+/+ (A–C), CHT−/− (D–F) and Hb9:CHT;CHT−/− (G–I) mice. Although weaker than CHT+/+, CHT immunoreactivity is present opposed to α-bungarotoxin staining in CHT−/−;Hb9:CHT diaphragms. Scale bar is 50μm. (J) Survival time from birth for mice of all six possible genotypes (CHT+/+ n=5, CHT+/− n=22, CHT−/− n=5, Hb9:CHT;CHT+/+ n=5, Hb9:CHT;CHT+/− n=22, Hb9:CHT;CHT−/− n=3). CHT+/+ open triangles; CHT+/− not shown, all survived to 4320 min; CHT−/− open circles; Hb9:CHT;CHT+/+ filled triangles; Hb9:CHT;CHT+/− not shown, all survived to 4320 min; Hb9:CHT;CHT−/− filled circles. (K–M) Photographs of mice at 4 hrs after birth. CHT−/−;Hb9:CHT mice have similar color to CHT+/+ mice and occasionally have a milk-spot (indicated by arrows) that is noticeably smaller in this pup.