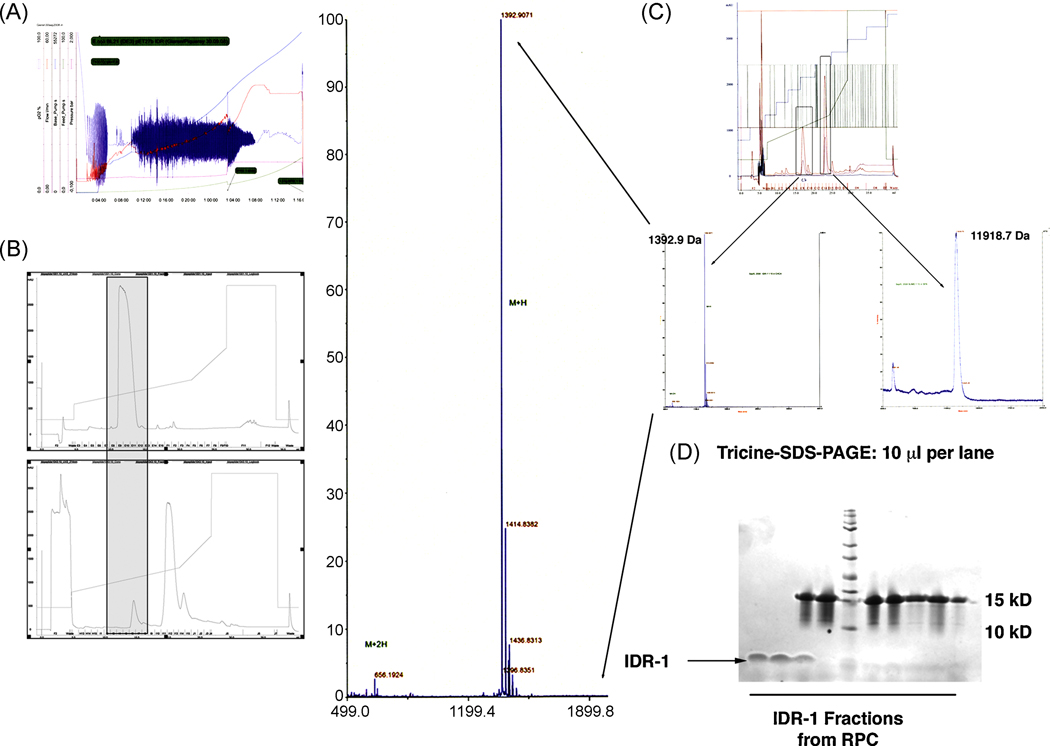
Figure 2.
A. Fermentation profile of a 10 L high-density fermentation of SUMO-IDR-1 using glucose-feed and IPTG induction for 14h. The fermentation yielded 1.5 kg biomass.
B. Comparison of the RP-chromatography profile for both the synthetic (upper panel) and recombinant IDR-1 peptide (lower panel). Both peptides eluted at the same percent of acetonitrile.
C. MALDI analysis of the purified IDR-1 peptide as well as the remaining his-SUMO protein after cleavage. The determined mass for IDR- 1 was identical to the synthetic peptide and the correct mass for his-sumo revealed 100 % cleavage using its protease sumoase. The MS profile for IDR-1 was magnified for better visualization.
D. Tricine-SDS-PAGE separation of the proteins from the recovered fractions from RP-chromatography shown in figure 2B. As can be seen in lanes 1 and 2, pure IDR-1 was recovered from fractions 11 and 12 followed by elution of SUMO in lanes 3–10). Lane 5 shows the Kaleidoscope Marker Plus (BioRAD).