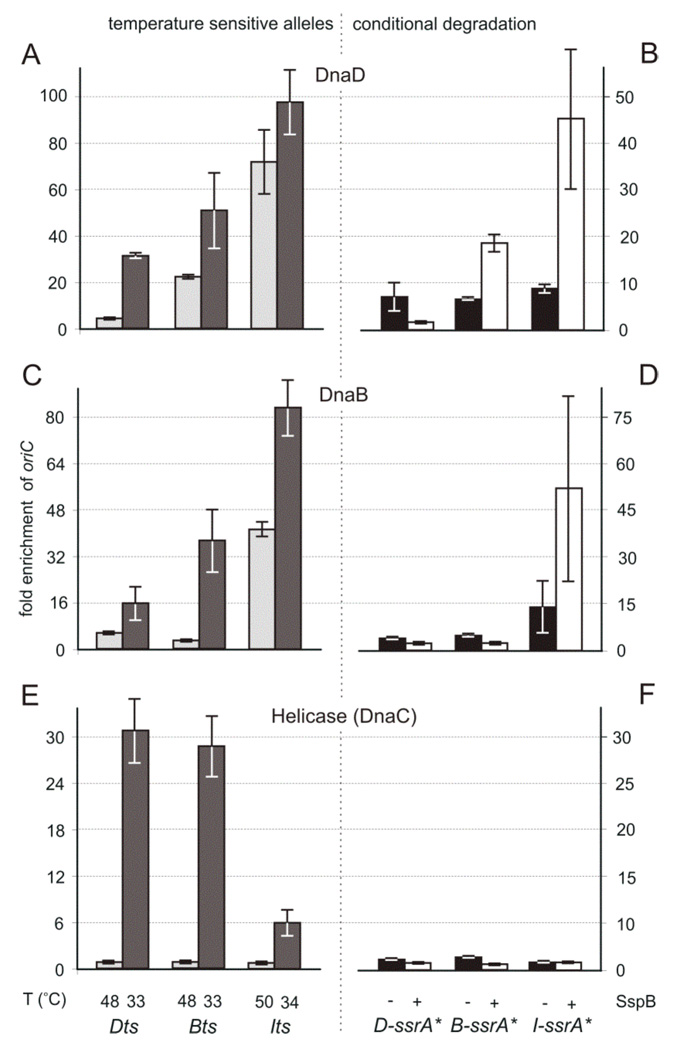
Figure 3. Order of dependence of DnaD, DnaB, and DnaC ( helicase) for association with oriC.
The relative enrichment of oriC after crosslinking and immunoprecipitation of the indicated proteins, DnaD (A, B), DnaB (C, D), and DnaC (E, F), was determined. Note the different scales on the y-axes. The indicated protein (x-axis) was inactivated by shift to non-permissive temperature (A, C, E) or expression of SspB to induce degradation of ssrA*-tagged proteins (B, D, F).
A, C, E. Temperature sensitive mutants included: dnaDts (KPL73), dnaBts (KPL69), and dnaIts (KPL147). Cells were grown at the permissive temperature, shifted to non-permissive (high) temperature (indicated) to inactive the mutant protein and allow ongoing rounds of replication to finish, and then shifted back to low temperature to allow replication to re-initiate. Samples were taken one hour after shift to high temperature (light gray bars) and 2 minutes after shift-down to permissive temperature (dark gray bars).
B, D, F. Conditional degradation mutants included: DnaD-ssrA* (WKS265), DnaB-ssrA* (WKS649), and DnaI-ssrA* (WKS738). Samples were taken for ChIP analyses during asynchronous exponential growth under permissive conditions, i.e., in the absence of inducer and little or no expression of SspB (black bars) and 1 hour after addition of inducer (IPTG or xylose) to induce expression of SspB and cause degradation of the indicated ssrA*-tagged protein. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (n=3).