Figure 5.
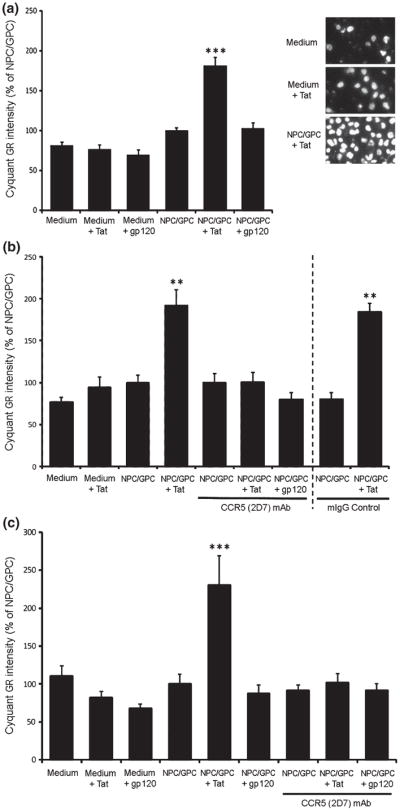
Chemotaxis of BV-2 cells and primary microglia in response to NPC/GPCs in transwell cultures. A. NPC/GPCs grown on a 24-well plate were treated with Tat or gp120 for 12 h prior to the addition of transwell inserts containing BV-2 cells. Transwell inserts were removed after 3 h, and cells crossing the insert membrane were labeled with CyQuantR GR dye and quantified on a PHERAstar FS plate reader with appropriate filters. Migration of BV-2 cells was not affected when either Tat or gp120 alone was added to the medium. Untreated NPC/GPCs also had no effect on BV-2 migration. However, the number of BV-2 cells moving across the transwell membrane was significantly enhanced when NPC/GPCs were pretreated with Tat for 12 h (*** p<0.001 vs. all other groups; N=6 independent cultures). Pretreatment of NPC/GPCs with gp120 did not affect BV-2 migration. The inset image shows Hoechst staining of BV-2 cells, and illustrates the effect of NPC/GPC treated with Tat to enhance migration. B. Antibody neutralization of CCR5 on BV-2 cells significantly attenuated Tat-enhanced migration. BV-2 cells on transwell inserts were pre-incubated with either 2D7 anti-CCR5 monoclonal antibody or control IgG2a for 1 h at 4°C, then placed into wells containing treated or untreated NPC/GPCs. Incubation with 2D7 antibody, but not control IgG2a, reduced BV-2 cell migration in the NPC/GPC+Tat treatment group back to basal levels. This suggests that the enhanced microglial migration caused by secretions from Tat-treated NPC/GPC is entirely mediated by CCR5-signaling. Antibody neutralization did not reduce migration in other treatment groups to below basal levels. (** p<0.01 vs. all other groups; N=6 independent cultures). C. Studies in A and B were repeated on primary murine microglia with similar results. Migration of primary microglia was significantly enhanced by the presence of NPC/GPCs pre-treated with Tat, although there was no effect of gp120 pre-treatment. Incubation with 2D7 antibody reduced migration in the NPC/GPC+Tat treatment group back to basal levels, but did not affect migration in other treatment groups. (*** p<0.001 vs. all other group; N=4 independent cultures).
