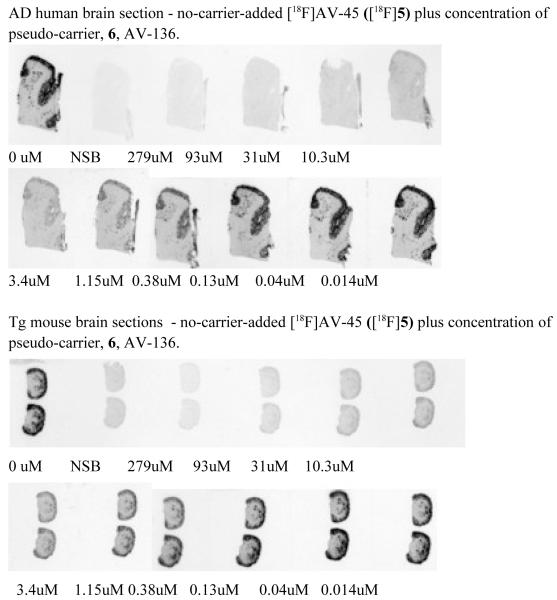
Fig. 2.
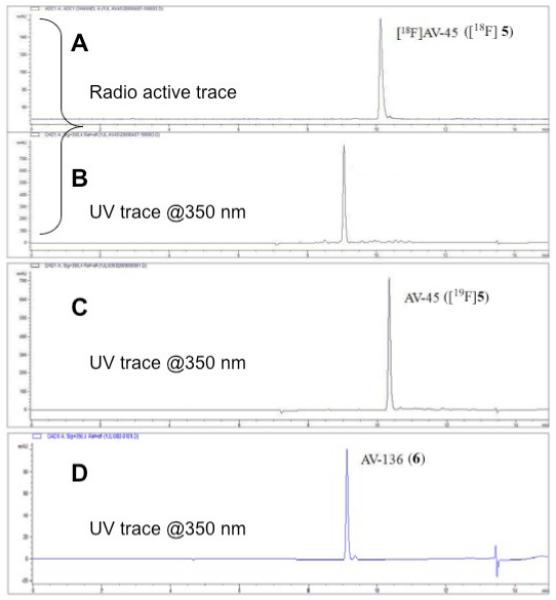
HPLC profile of a [18F]AV-45 ([18F]5) sample purified by SPE method (trace A: radio trace of sample; trace B: UV trace of sample @ 350 nm). Trace C is an UV trace of non - radioactive reference compound AV-45 (@350 nm). The bottom trace (D) is an UV trace of AV-136 (6) (@350 nm).
HPLC profile of [18F]AV-45 ([18F]5) sample purified by SPE method (HPLC conditions: Agilent HPLC 1100 ; Gemini C18 column (250mm × 4.6 mm); mobile phase: 1 mL/min with a gradient as follows: from 0 – 2 min isocratic 10 mM ammonium formate buffer (AFB) 100%; from 2 - 5min gradient AFB 100 - 30%, ACN 0 - 70%; from 5 - 10 min gradient AFB 30 - 0%, ACN 70 - 100% and from 10 - 15 min AFB 100%).
A: radioactive trace of sample
B: UV trace of sample @ 350 nm
C: UV trace of cold AV-45 ([19F]5) under identical HPLC conditions as above.
D: UV trace of synthesized AV-136 @ 350 nm under identical HPLC conditions as above. The “identical” retention times of AV-136 compared to the UV material of the labeled sample suggest that the byproduct in the labeling is AV-136 (6).