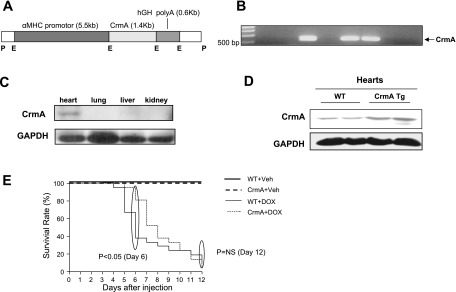
Fig. 1.
Generation of cytokine response modifier A (CrmA) transgenic (Tg) mice and survival of doxorubicin (Dox)-induced cardiomyopathy in wild-type (WT) and CrmA Tg mice. A: schematic diagram of the construct used to generate Tg mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of CrmA. Cardiac-specific expression was achieved using α-myosin heavy chain (α-MHC) promoter. B: genotyping of CrmA Tg mice. CrmA Tg mice were identified by the appearance of a 525-bp band in tail genomic DNA. C: representative Western immunoblot analysis of different tissues from CrmA Tg mice. GAPDH was used as an internal control. D: representative Western immunoblot analysis of heart tissues from WT and CrmA Tg mice hearts. E: 12-day survival curves for WT and CrmA Tg mice after Dox (20 mg/kg) or vehicle (Veh) injection; n = 6 mice/group (Veh) and 21/group (Dox). The early term survival of WT/Dox mice was significantly less than CrmA/Dox mice (at day 6, P <0.05 by Wilcoxon's test), but the Dox groups did not differ at day 12. hGH, human growth hormone; P, Pvul; E, EcoR1; polyA, polyandenylation; NS, not significant.