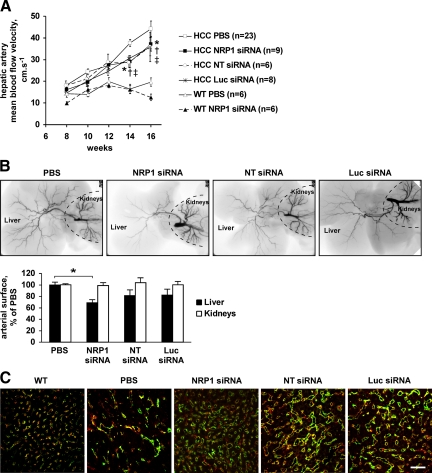
Figure 2.
Both NRP1 and control siRNAs inhibit tumor angiogenesis and vascular remodeling in HCC mice. A: Time average mean BFV in the hepatic artery of treated mice was estimated using Doppler ultrasound imaging. Both NRP1 and control siRNAs significantly delayed the increase in hepatic artery BFV indicating inhibition of tumor vasculature remodeling. *P < 0.05 (NRP1 siRNA versus PBS); †P < 0.05 (NT siRNA versus PBS); ‡P < 0.05 (Luc siRNA versus PBS) (Student’s t-test). B: A contrast agent was injected into the aorta of treated mice and the arterial phase in the liver and kidneys was analyzed using microangiography. Arterial vessel density was quantified with a PRIMed Angio v0.9 software. As evident by microangiography, NRP1 siRNA and to a lesser extent control siRNAs inhibited arterialization of the blood supply in HCC mice. *P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). C: CD31 (green) and NRP1 (red) double immunostaining of liver sections harvested from mice at 16 weeks. In mice treated with siRNAs, liver vascularization was characterized by more regular, less fused sinusoids that resemble those in wild-type liver (left micrograph). Scale bar, 50 μm.