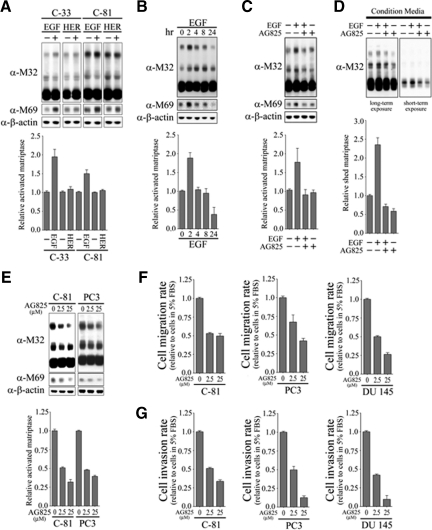
Figure 2.
Effects of EGF and heregulin-β1 on matriptase zymogen activation and shedding in C-33 LNCaP cells. A: Effects of EGF and heregulin-β1 on matriptase zymogen activation in C-33 LNCaP cells. LNCaP C-33 cells were seeded at a density of 1 × 106 per well in each 6-cm dish. Two days after plating, cells were starved with serum-free medium for 36 hours. After treatment with 20 ng/ml EGF or 40 ng/ml heregulin-β1 for 2 hours, cell lysates were collected under nonboiling and nonreducing conditions and immunoblotted for matriptase and activated matriptase with anti-total matriptase (M32) and anti-activated matriptase (M69) mAbs. B: Kinetics of EGF-stimulated matriptase activation in C-33 LNCaP cells. Starved cells were treated with 20 ng/ml EGF for 0, 2, 4, 8, or 24 hours. Cell lysates were then prepared and used to assay total and activated matriptase with anti-total matriptase (M32) and anti-activated matriptase (M69) mAbs. C: Serum-starved cells were treated with or without 20 ng/ml EGF in the presence or absence of 2.5 μmol/L AG825 for 2 hours. The immunoblots were performed as described in B. D: Conditioned media were collected from the cells treated with or without 20 ng/ml EGF in the presence or absence of 2.5 μmol/L AG825 for 24 hours. The immunoblots were performed as described in B. The levels of secreted matriptase were quantitated by using a densitometer and normalized to their respective cell numbers. E: The effect of AG825 on matriptase activation in C-81 LNCaP cells (left panel) and PC-3 cells (right panel). Starved cells were treated with AG825 at 0, 2.5, and 25 μmol/L for 24 hours. The immunoblots were performed as described in B. The effects of AG825 on cell migration (F) and invasion (G). After cell seeding into transwells, LNCaP C-81, PC3, and DU145 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of AG825. Cell migration and invasion assays were performed, according to the protocol, as described in Figure 1A.