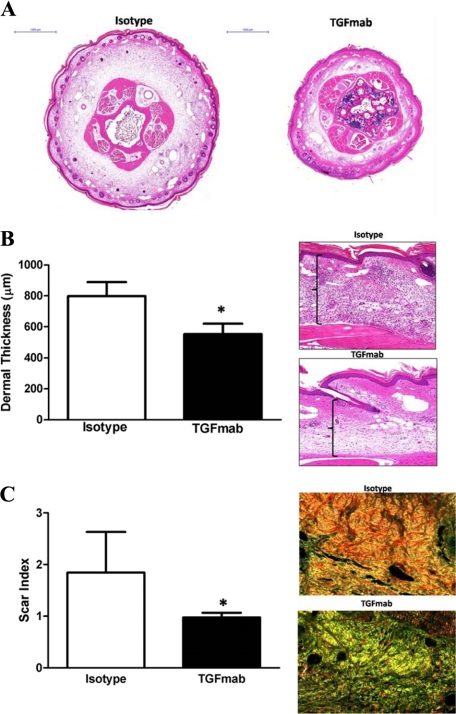
Figure 3.
Systemic TGF-β1 blockade decreases tissue fibrosis secondary to lymphatic fluid stasis. A: Representative cross-sectional histology of isotype- (left) and TGFmab-treated animals 6 weeks after surgery. Twofold magnification of both sections is shown. Note marked increase in ECM deposition, hypercellularity, and dilated lymphatics in isotype-treated animals. B: Dermal thickness measurement in isotype- and TGFmab-treated animals (mean ± SD; *P < 0.001). Representative figures of high-power (20×) views of longitudinal sections from isotype- (top) and TGFmab- (bottom) treated animals. C: Scar index calculation in isotype- and TGFmab-treated animals in tissues distal to the zone of lymphatic obstruction harvested 6 weeks after surgery (mean ± SD; *P < 0.01). Representative 20× micrographs demonstrate a predominantly red/orange birefringence (consistent with increased fibrosis) in isotype-treated animals (top). In contrast, TGFmab-treated animals demonstrate primarily a yellow/green birefringence, indicating normal ECM deposition.