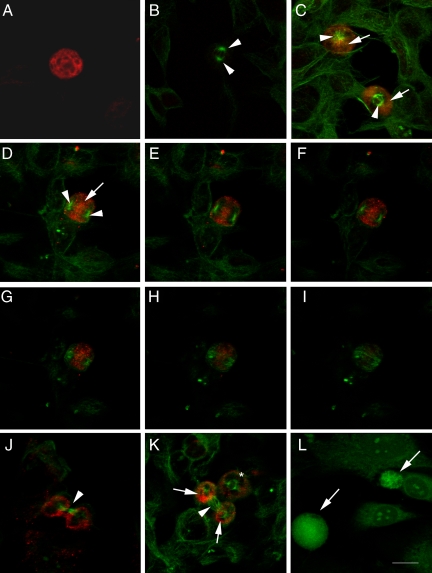
Figure 2.
MMP-9 immunoreactivity and the mitotic spindle labeled with β-tubulin. Confocal microscope images showing MMP-9 immunoreactivity (red in A–K and green in L) and/or β-tubulin (green in A–K). The monoclonal antibody against MMP-9 was either from Oncogene (A) or Chemicon International (B–L). Cells in A–K are SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, whereas cells in L are mouse fibroblasts. A: Single immunocytochemistry against MMP-9 shows strong MMP-9 immunostaining in a cell at prophase. B: Negative control for double immunocytochemistry against MMP-9 and β-tubulin, in which the primary antibody against MMP-9 was omitted. Arrows show the two poles of the mitotic spindle in a dividing cell. C: Cells at prophase (top) and metaphase (bottom) showing MMP-9 (red, arrows) located behind the centrosomes (green, arrowheads). D–I: Cell at anaphase showing MMP-9 (red, arrow) between the two poles (arrowheads) of the mitotic spindle (green). D: Projection image. E–I: Sequential 0.5-μm sections through the cell. J: Cell at cytokinesis showing the two separated daughter cells surrounded by MMP-9 immunoreactivity and connected by the rest of the spindle microtubules at the segmentation sulk (arrow). K: Cell at prometaphase (asterisk) and cell at cytokinesis showing two clearly distinguished MMP-9-immunostained areas (red, arrows) surrounding the two daughter cells, which are connected through the microtubules of the spindle (arrowhead). L: MMP-9 staining (green) is stronger in dividing (arrows) than in resting fibroblasts. Arrows (C–K) point to zones of MMP-9-immunoreactivity, and arrowheads point to the tubulin-positive mitotic spindle in dividing cells. Arrows in L point to MMP-9-positive cells. Scale bar = 15 μm.