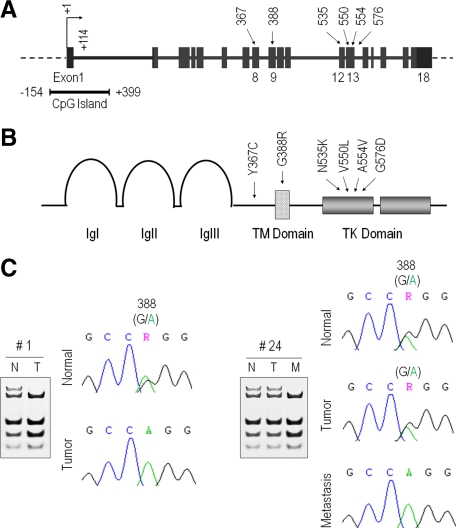
Figure 1.
FGFR4 gene structure, genomic sequencing, and encoded proteins. A: The FGFR4 coding exons are shown in boxes with the transcription start site indicated by a bent arrow. The 5′-associated CpG island spanning the indicated region is shown immediately below and to the left. Previously described FGFR4 intragenic mutations are illustrated by arrows with corresponding exons marked immediately below and the codon number above. B: The corresponding FGFR4 protein sequence is shown with the extracellular Ig-like domains labeled as Ig(s). TM is the transmembrane domain, and TK is the tyrosine kinase domain. The intragenic mutations are labeled by arrows with the corresponding codon numbers shown immediately above. The FGFR4 germline SNP is represented by G388R, reflecting a glycine to arginine substitution. C: Comparison of paired normal (N) and tumorous (T) breast cancer sample DNA sequences at FGFR4 codon 388. The patient to the left (no. 1) depicts a heterozygous G/R pattern in normal breast with retention of only the R allele in the corresponding tumor. The patient to the right (no. 24) is heterozygous for the FGFR4-G388R SNP in the normal (N) breast and primary tumor (T). The associated lymph node metastasis (M) demonstrates loss of one of the FGFR4-WT allele. A summary of findings is compiled in Table 1.