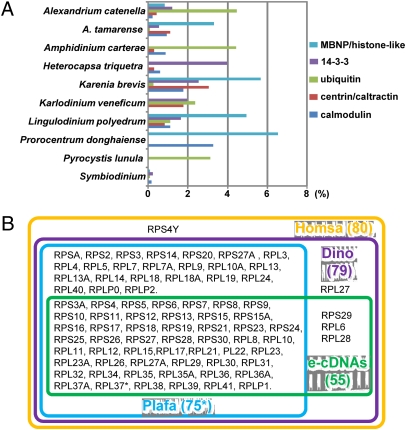
Fig. 2.
Comparative analyses of common and highly expressed genes between e-cDNAs and reported datasets. (A) Taxonomic distribution (y axis) among the previously studied dinoflagellates and relative expression levels (x axis; percentage of the transcript in total number of transcripts examined for the species) of the five most highly expressed common genes in e-cDNAs. (B) Dinoflagellate RP set (Dino, purple box) identified from e-cDNAs (green box) and existing DinoEST, which is four proteins more than that in Plasmodium falciparum (Plafa, blue box), one (the Y chromosome–associated RPS4) less than that in humans (Homsa, yellow box), and one (RPLP3) less than that in plants. Asterisks depict that RPL37 is shown not to exist in P. falciparum in the RP database, but we found it in GenBank (Table S4).