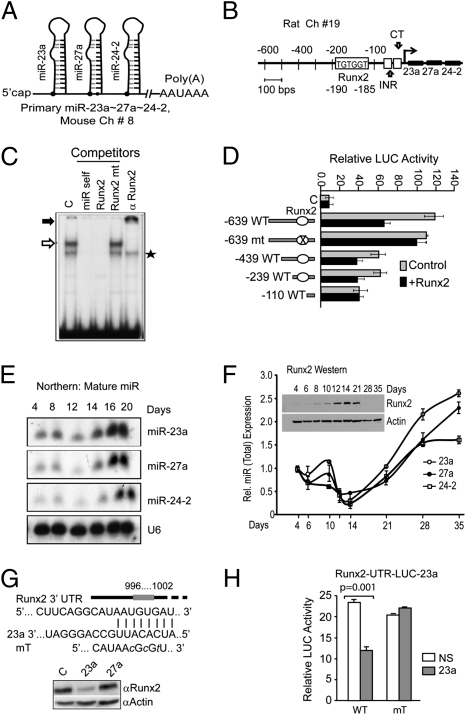
Fig. 1.
A functional Runx2 DNA binding site regulates expression of the miR-23a∼27a∼24-2 cluster and miR-23a regulates Runx2. (A) Stem loop structure of the transcript for the murine miR cluster in chromosome 8. (B) Representation of the rat −0.639-kb miR-23a∼27a∼24-2 cluster promoter fragment. Transcription factor analysis of the proximal promoter showing the Runx binding site by TRANSFAC, TESS program (TGTGGT, −185 to −190 for rat), the INR motif (initiator, CCCCACCTCC), and the CT motif (CTCT…) sequence at −56 to −34 (23). (C) EMSA of nuclear proteins from MC3T3-E1 cells using an oligonucleotide WT and mutant probe (Table S1) for the Runx2 site in the miR promoter. Control binding (C, lane 1), self-competitor for WT (miR self, lane 2), Runx2 consensus WT (Runx2, lane 3) or mutant (Runx2 mt, lane 4), and antibody supershift (lane 5) are shown. Open arrow, Runx2 complex; solid arrow, supershifted Runx2 protein–DNA complex; star, NS band. (D) Functional activity of the Runx2 site in the −0.639 kb human miR cluster promoter and its deletion and mutant constructs with luciferase reporter. The reporter constructs were cotransfected with control vector (gray bars) or Runx2 expression construct (solid black bars) in MC3T3-E1 cells (Materials and Methods describes quantification). (E) Northern blot for expression of mature miR-23a, -27a, and -24-2 during primary ROB cell differentiation (days 4–20). U6 was used for control. (F) Expression of the miR cluster by qPCR and Runx2 protein (Inset; Western). (A) Total RNA from ROB cells was assayed for each miR (precursor and mature) normalized to U6 expression as indicated. Runx2 protein detected by a mouse monoclonal antibody (MBL International). Actin was used for control. (G) Upper: Diagram of the 3′ UTR of Runx2 mRNA illustrating miR-23a binding site and a mutation (mT). Lower: Western analysis of Runx2 protein in day 20 ROB cells transduced on day 4 with lentiviral overexpression of miR-23a and -27a. Actin was used as loading control. (H) Runx2 3′ UTR LUC assay demonstrating miR-23a regulation using MC3T3-E1 cells (Materials and Methods).