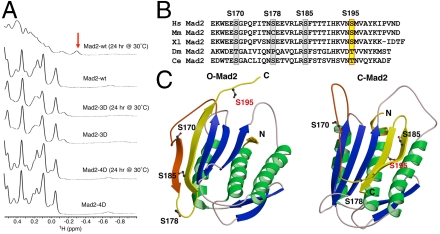
Fig. 1.
The phospho-mimicking mutants of Mad2 fail to undergo the O─C conformational transition. (A) The high-field region of the 1D 1H spectra of wild-type Mad2 (Mad2-wt) or its phospho-mimicking mutants, Mad2-3D and Mad2-4D, before and after a 24-hr incubation at 30 °C. Mad2-3D contains S170D, S178D, and S195D mutations. Mad2-4D contains S170D, S178D, S185D, and S195D mutations. The -0.3 ppm peak that is unique to V197 in C-Mad2 is indicated by an arrow. (B) Sequence alignment of the C-terminal region of Mad2 proteins from Homo sapiens (Hs), Mus musculus (Mm), Xenopus laevis (Xl), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm), and Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce). (C) Ribbon drawing of the structures of O-Mad2 and C-Mad2. The α-helices are colored green, β-strands blue, and loops ivory. The structural elements of Mad2 that undergo major changes are in yellow and orange. S170, S178, S185, and S195 are shown as ball-and-stick.