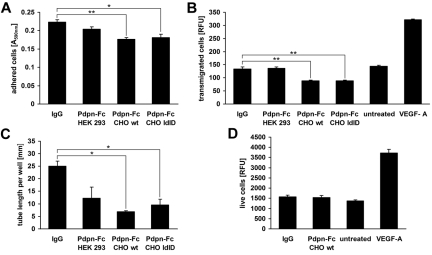
Figure 1.
Podoplanin-Fc inhibits functions of LECs in vitro. (A) Primary human LECs were allowed to adhere to type I collagen-coated cell culture plates for 45 minutes in the presence of 0.5μM podoplanin-Fc glycoforms or human IgG. Attached cells were stained with crystal violet and the absorbance of subsequently resolubilized dye was measured at 590 nm. (B) Haptotactic migration of LECs toward type I collagen was assessed in a 2-chamber assay for 3 hours in the presence of 0.5μM podoplanin-Fc glycoforms or human IgG. Chemotactic migration toward 20 ng/mL VEGF-A served as positive control. Transmigrated cells were stained with calcein and fluorescence intensity (RFU) at λex 485 nm/λem 539 nm was measured. (C) Tube formation by LECs was assessed in type I collagen gels containing 0.5μM podoplanin-Fc glycoforms or human IgG. The length of tube-like structures was determined after 14 hours in three 5× magnified images per well. (D) Proliferation of LECs was assessed in the presence of 0.5μM podoplanin-Fc from CHO wild-type cells or human IgG, or 20 ng/mL VEGF-A. Live cells were stained after 48 hours with 4-methylumbelliferyl heptanoate and fluorescence intensity (RFU) at λex 355 nm/λem 450 nm was measured. Data represent mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3 [A-C] or n = 8 [D]), ** P < .01, * P < .05.