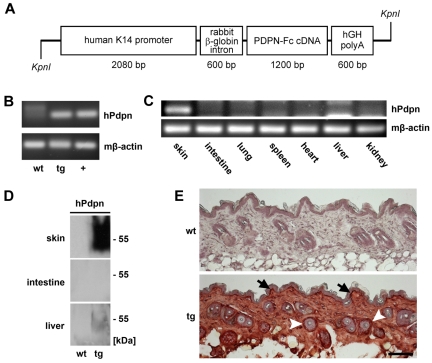
Figure 4.
Targeted overexpression of podoplanin-Fc in the skin of transgenic mice. (A) Schematic representation of the K14 podoplanin-Fc transgene construct. (B) Human podoplanin mRNA was detected by RT PCR using total RNA (200 ng) extracted from the skin of wild-type and K14 podoplanin-Fc transgenic mice. RNA (100 ng) from mouse cells transfected with human podoplanin cDNA was used as positive control (+). (C) Human podoplanin mRNA was detected by RT PCR using total RNA (300 ng) extracted from different organs of K14 podoplanin-Fc transgenic mice. (D) Podoplanin-Fc (50-55 kDa) was detected by immunoblot analysis of tissue lysates from skin, intestine, and liver of wild-type and transgenic mice. (E) Podoplanin-Fc was detected by immunohistochemical analysis of paraformaldehyde-fixed cryosections of dorsal skin samples taken from wild-type and transgenic mice at 6 weeks of age. It was expressed at high levels in the basal keratinocyte layer (arrows) and in the outer root sheath keratinocytes of hair follicles (arrowheads). Bar represents 100 μm. Immunoblot and immunohistochemical analyses were performed using antibodies directed against human podoplanin. wt wild-type; tg transgenic; hPdpn human podoplanin.