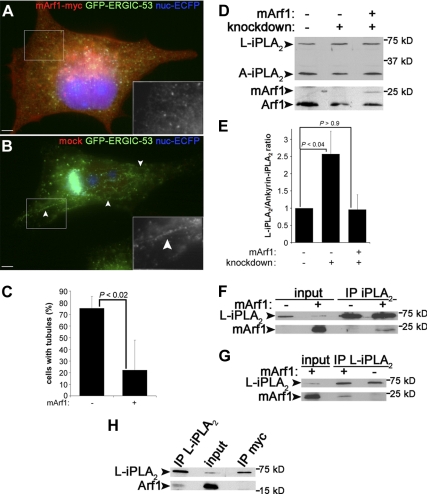
Figure 5.
mArf1 rescues Arf1+Arf4 knockdown and interacts with PLA2G6-A. (A) Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells as described in Figure 1D were transfected with mArf1 and stained with anti-myc. (B) Cells as described in A mock transfected. Insets are magnifications of GFP-ERGIC-53 channel in the highlighted regions. Arrowheads point to tubules. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Knockdown cells were counted as described in Figure 3F. Data are represented as mean ± SD from four to five independent experiments. The p value was calculated with a Wilcoxon rank test. (D) Same immunoblots as shown in Figure 4C with the rescue condition in addition. (E) Quantification of the ratio L-iPLA2 to ankyrin-iPLA2 as described in Figure 4D. Results are shown as mean ± SEM from four to eight independent experiments. p values were calculated using a Student's t test. (F) Cells transfected (+) or not (−) with mArf1 were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-PLA2G6-A (IP iPLA2) and blotted with anti-PLA2G6-A (top) or anti-myc (bottom). The total lysate (1%) is shown as a loading control. (G) Cells were processed as described in F and immunoprecipitated with anti-L-iPLA2 antibody (IP L-iPLA2). They were then immunoblotted as described in F. (H) Cells as described in F were immunoprecipitated with anti-L-iPLA2 antibody or as a negative control with anti-myc antibody. They were then immunoblotted with anti-PLA2G6-A (top) or anti-Arf1 (bottom).