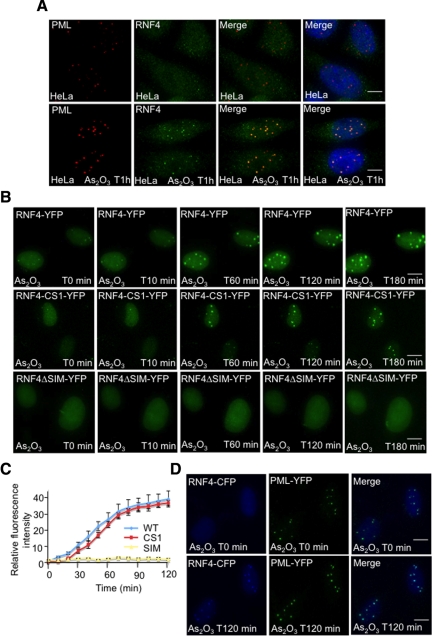
Figure 5.
Arsenic-induced SUMO-dependent recruitment of RNF4 into PML nuclear bodies. (A and B) Subcellular localization of RNF4 during arsenic treatment. (A) HeLa cells were exposed to 1 uM arsenic for 60 min and the localization of endogenous PML and RNF4 determined by immunofluorescence using 5E10 mAb to PML and an affinity purified chicken antibody to RNF4. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with fluorescent-tagged RNF4 plasmids expressing either wild type RNF4-YFP or protein mutated in the RING domain of RNF4 (RNF4-YFP-CS1) or RNF4 with all 4 SIMs mutated (RNF4-delta SIM). YFP fluorescence (green) was monitored in real-time microscopy after arsenic treatment by collecting a stack of 20 z-sections every 10 min for 3 h. Images represent a projection of the z-sections. (C) Quantification of RNF4-YFP fluorescence was determined by measuring the difference of fluorescence intensity between one PML body and a region outside the nucleoplasm. The graph shows means values of the relative fluorescence intensity after normalization from 10 cells. (D) Arsenic-induced recruitment of RNF4 in HeLa PML-YFP stable cells. PML-YFP HeLa cells were transfected with a RNF4-CFP plasmid and fluorescence monitored for 2 h after addition of arsenic. Images shows the recruitment of RNF4-CFP (blue) within PML bodies (green). Bar, 5 μM.