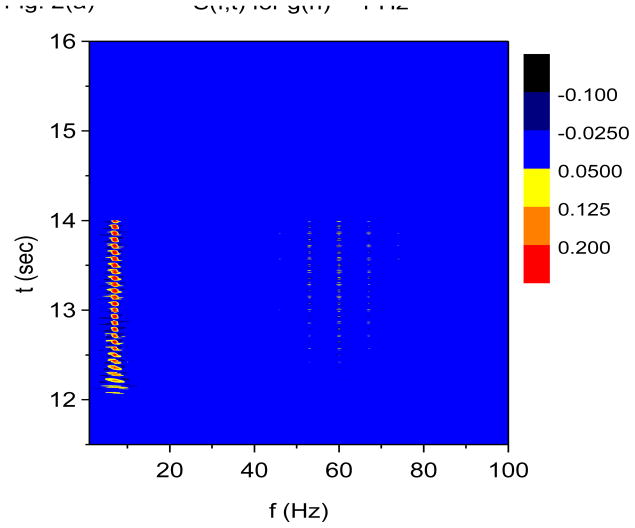
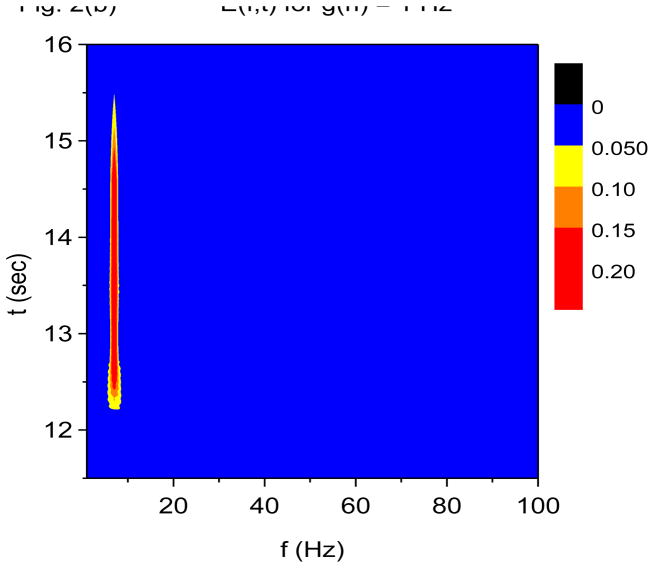
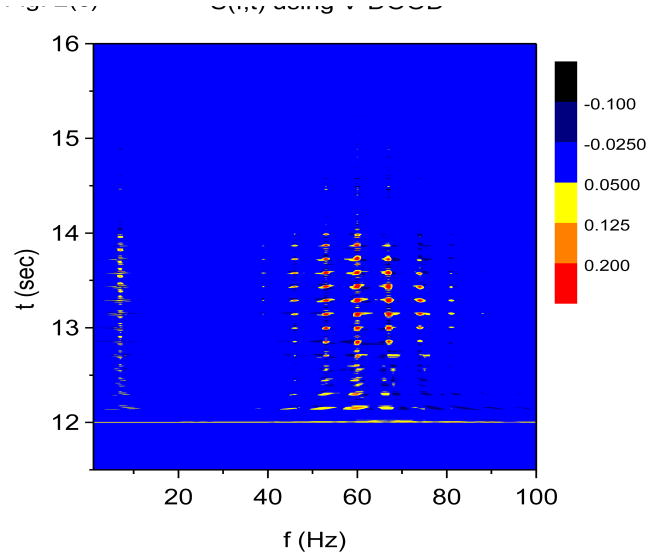
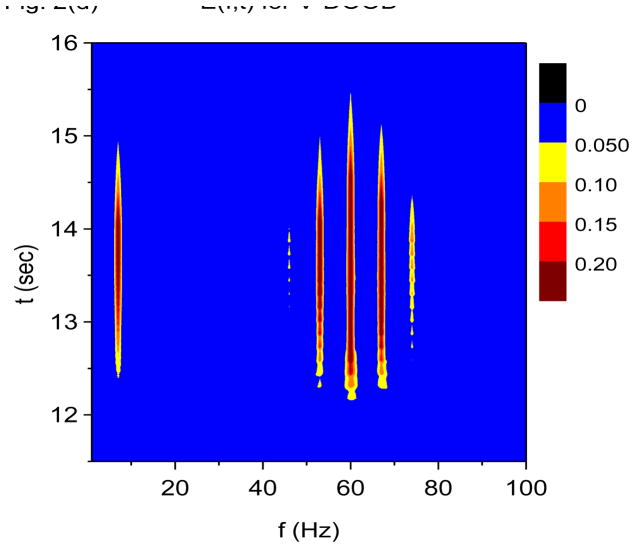
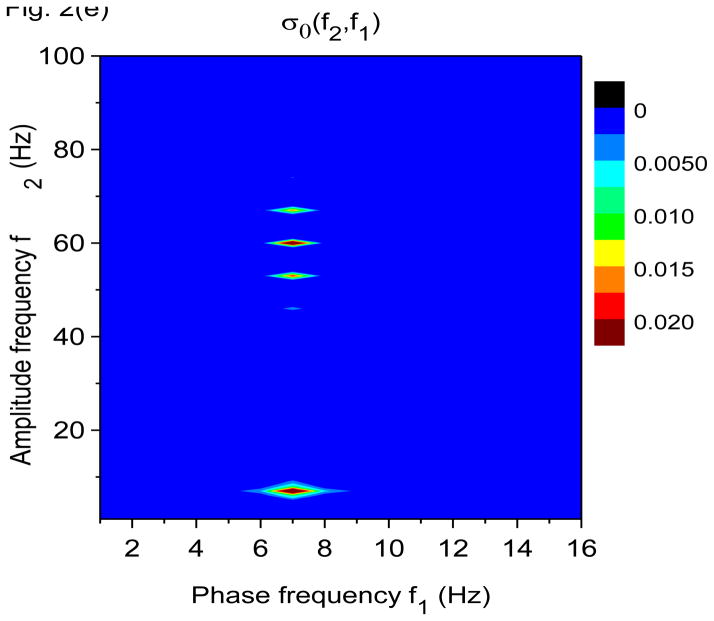
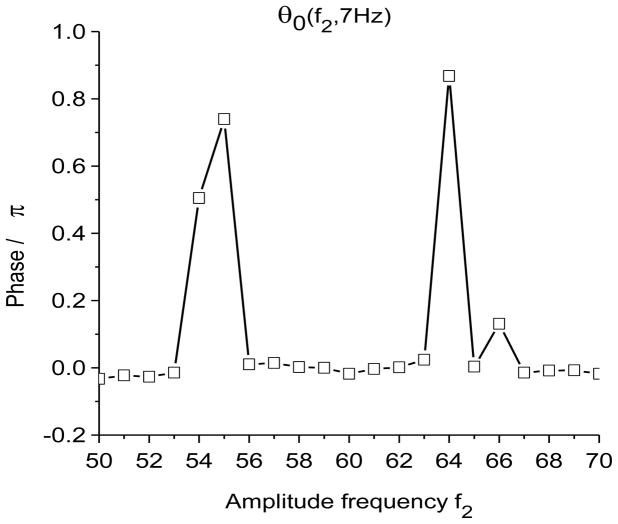
Figure 2.
Time-frequency and phase-amplitude analysis applied to computer generated data. The friction is g(n)=1 Hz for all n, except for (e) and (f) where g(n)= 0 for all n. In these graphs, S(f, t) and E(f, t) are rescaled so that the maximum value is equal to one. (a) Time-frequency plot for S(f, t) using X-DOOD, h(t) = xdata (t). (b) Time-frequency plot for E(f, t) using X-DOOD, h(t) = xdata (t). (c) Time-frequency plot for S(f, t) using V-DOOD, h(t) = ẋdata (t). (d) Time-frequency plot for E(f, t) using V-DOOD, h(t) = ẋdata (t). (e) Phase amplitude correlation function σ0 (f2, f1) using X-DOOD. (f) Relative phase θ0(f2, 7 Hz) as a function of amplitude frequency f2.