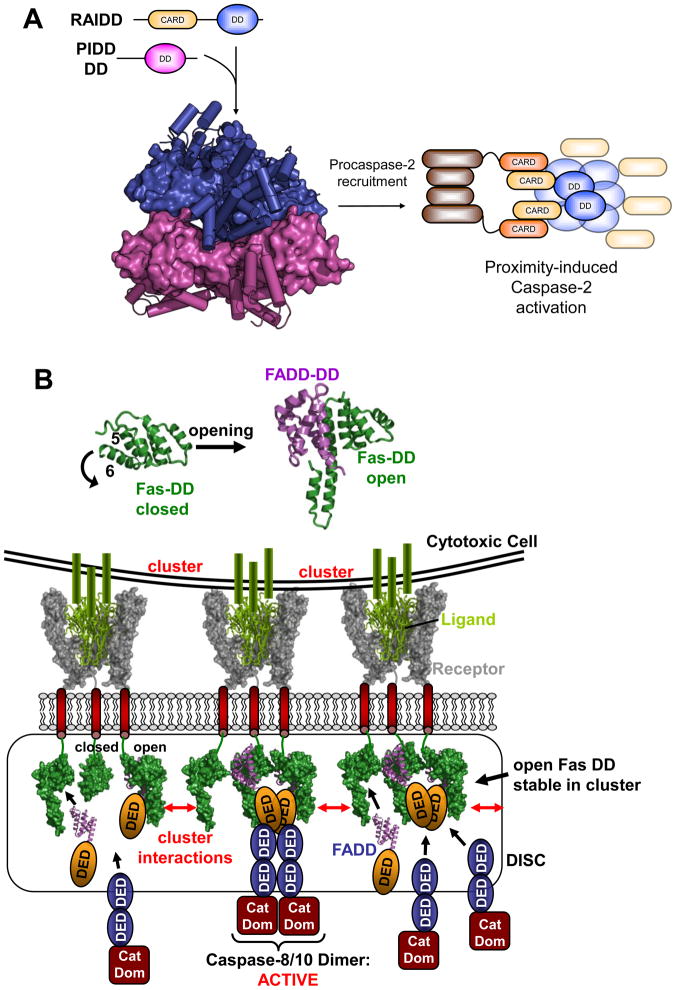
Figure 2. Death Domain assemblies: PIDDosome and DISC.
A. PIDDosome. Following processing to remove the N-terminal LRR and ZU5 domains of full-length PIDD, its C-terminal DD forms the PIDDosome along with RAIDD. Pentameric rings of PIDD (magenta) and RAIDD (blue) DD form extensive contacts and an additional two RAIDD DD bind atop the RAIDD ring (PDB entry 2of5). DD are shown alternately in surface and cartoon representation for clarity. The CARD domains of RAIDD then recruit procaspase-2 to facilitate proximity-induced dimerization and activation.
B. DISC formation: DD opening and illustrative rendering of Death Receptor clustering. Top: DD of the Death receptor Fas is adopting the classic globular shape comprised of six helices (left). In order to bind the DD of the adaptor protein FADD (magenta) the DD of Fas (green) has to undergo an opening mechanism where helix 6 moves outward and fuses with helix 5 (right). Bottom: Illustration of receptor clustering and DISC formation. The structure of a TRAIL (green)/TRAIL receptor (grey) complex [79] is used to illustrate a cell presenting clustered ligands leading to a clustering of receptor trimers in the target cell. On the insight of the affected cell DDs (from Fas DD structures) are brought into close proximity. Open Fas forms can interact and stabilize each other and are able to recruit FADD. FADD in turn recruits and activates target caspases via DED interaction (based on PDB entries: 1d0g, 1ddf, 3ezq).